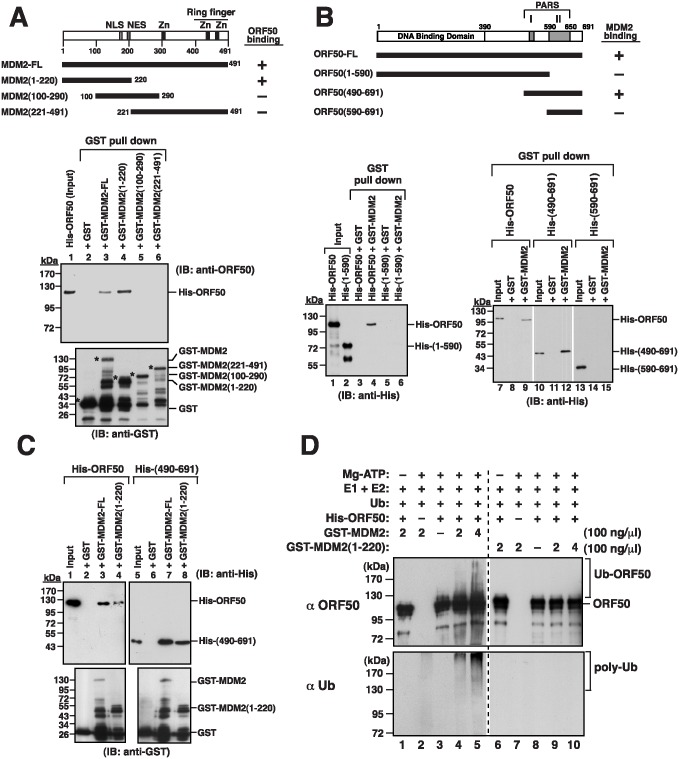
Fig 10. Mapping of the interaction domains between MDM2 and ORF50, and ubiquitination of ORF50 by MDM2 in vitro.
(A) Defining the ORF50-interacting domain of MDM2. The purified His-tagged ORF50 (His-ORF50) was incubated with GST, GST-MDM2 or GST-MDM2 deletion mutants (1–220, 100–290 and 221–491) expressed in E. coli. Following pull-down with glutathione beads, the pull-down lysates were immunoblotted with anti-ORF50 or anti-GST antibody. (B) Defining the MDM2-interacting domain of ORF50. Glutathione beads conjugated to GST-MDM2 were incubated with His-ORF50 or His-ORF50 deletions as shown in the diagram. The GST pull-down precipitates were immunoblotted using anti-His antibody. (C) Detection of the interaction between GST-MDM2(1–220) and His-ORF50(490–691) in pull-down assay. (D) Effect of MDM2 on ORF50 ubiquitination in vitro. The in vitro ubiquitantion assay was performed using purified components as indicated. In the reactions, purified His-ORF50 protein was used at a final concentration of 120 nM and GST-MDM2 (or GST-MDM2(1–220)) at 100 nM or 200 nM. Reaction mixtures were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-ORF50 or anti-Ub antibody.