FIGURE 1.
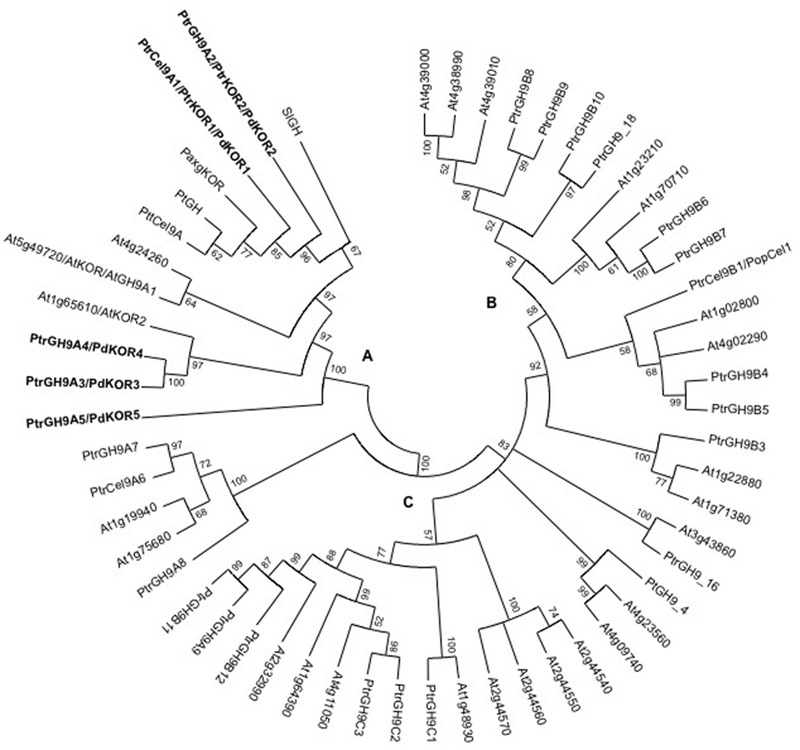
Phylogenetic analyses of endo-β-1,4-glucanases from Populus, Arabidopsis and selected KOR-like genes from other species using MEGA5 program. The evolutionary history was inferred by using the Maximum Likelihood method based on the JTT matrix-based model. The percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (500 replicates) are shown next to the branches. The three distinct branches are represented by (A–C) subgroups. KORs from this study are in bold. The analysis involved 55 predicted protein sequences and the corresponding accession numbers are: At4g39000; At4g38990; At4g39010; At1g70710; At1g23210; At4g02290; At1g02800; At1g22880; At1g71380; At4g23560; At4g09740; At3g43860; At1g64390; At4g11050; At2g32990; At1g48930; At2g44570; At2g44560; At2g44540; At2g44550; At1g75680; At1g19940; At1g65610/AtKOR2; At5g49720/AtKOR/AtGH9A1; At4g24260; PaxgKOR (Populus alba x grandidentata): ADB82903.1; PtGH (P. tremuloides): AAS45400.1); PtrKOR1/PdKOR1 (P. trichocarpa, Potri.003G151700); PtrKOR2/PdKOR2 (Potri.001G078900); PtrKOR3/PdKOR3 (Potri.008G079500); PtrKOR4/PdKOR4 (Potri.010G177300); PtrKOR5/PdKOR5 (Potri.005G188500); PtrCel9A6 (Potri.005G237700); PtrGH9A7 (Potri.002G023900);PtrGH9A8 (Potri.005G115400); PtrGH9A9 (Potri.002G225200); PtrCel9B1/PopCel1 (Potri.001G083200); PtrGH9B3 (Potri.019G069300); PtrGH9B4 (Poptri.014G126900); PtrGH9B5 (Potri.002G202400); PtrGH9B6 (Potri.010G109200); PtrGH9B7 (Potri.008G132700); PtrGH9B8 (Potri.009G123900); PtrGH9B9 (Potri.004G162200); PtrGH9B10 (Potri.015G12800); PtrGH9B11 (Potri.014G157600); PtrGH9B12 (Potri.001G356000); PtrGH9C1 (Potri.007G071200); PtrGH9C2 (Potri.003G139600); PtrGH9C3 (Potri.001G092200); PtGH9_4 (Potri.001G098800); PtrGH9_16 (Potri.006G219700); PtrGH9_18 (Potri.015G127900); PttCel9A (P. tremula x tremuloides):AAT75041.1); SlGH (Solanum lycopersicum): AAC49704.1
