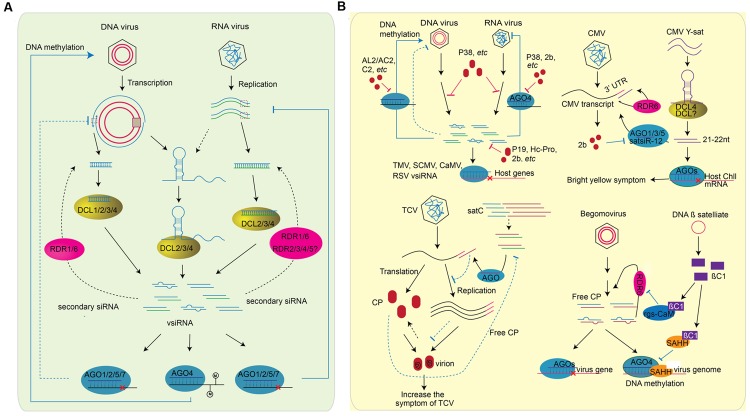
FIGURE 3.
Role of sRNAs in plant-virus interaction. RNA silencing inside plant cells can be divided into two parts: (A) Plant generate vsiRNAs, targeting on virus genome directly to defend viral infection. The generation of vsiRNA are slightly different for RNA virus or DNA virus. For RNA virus, the structure region of virus genome, dsRNA replicative intermediate forms of ssRNA viruses, and the dsRNA genomes of dsRNA viruses can be processed by DCL proteins (right). The vsiRNAs of DNA virus, on the other hand, can be processed from the structured region of the transcript and the overlapping region of the bi-direction transcription (left). In both cases, RDR1 and RDR6 are involved in the generation of secondary vsiRNA (shown in blank dash line). After generation, vsiRNAs are loaded into different AGOs and perform the silencing of virus genome. vsiRNAs target on RNA virus to slice the genomic RNA, while perform DNA methylation on the genome of DNA virus. Whether vsiRNA targets on the transcription of DNA virus remains unknown (blue dash line). (B) The counter-defense of virus to plant RNA silencing machinery. As plant generates vsiRNA to silence virus genome, viruses encode suppressors, such as 2b, Hc-Pro, P19, AL2/AC2, P38, and etc., as a counter-defense (left above). The effect of suppressor on RNA silencing include the interfere of DCL slicing, the blocking of methylation, the binding of vsiRNsA, the preventing of RISC assembly, and etc. vsiRNAs encoded by TMV, CMV, CaMV, and RSV can also target the host genes to decrease plant defense. In addition, plant viruses are often accompanied with a variety of subviral RNA/DNAs. These satellite RNA/DNAs affect virus pathogenicity by generating satRNA-derived siRNAs (satsiRNAs). CMV Y satellite (Y-sat) produces a 22-nt satsiRNA that targets Chll, a key gene involved in chlorophyll synthesis, resulting in bright yellow symptom. sat-siR-12, another satsiRNA can loaded into AGO1/3/5 and regulate CMV transcripts accumulation with the function of RDR6. As counter defense, CMV encodes VSR 2b to inhibit the function of AGOs (right above). TCV is often accompanied with a single strand satellite RNA (satC) that is composed of the 3′ end of TCV helper virus (left bottom). Because of the sequence similarity of satsiRNA and the 3′ end of TCV helper virus, the presence of satC-siRNA represses the accumulation of TCV genomic RNA. At the same time, TCV genomic RNA and the CP protein assemble to a virion. CP is a VSR encode by TCV. The down-regulation of TCV transcripts by satC-siRNAs result in the increase of free CP protein, which subsequently suppresses the accumulation of satC-siRNAs (shown in dash line). DNA ß satellites are circular ssDNA that associate with many monopartit begomoviruses. The ßC1 protein encoded by DNAß satellite is a VSR that suppresses TGS by the interaction with SAHH, and PTGS through the interaction with rgs-CaM (right bottom).