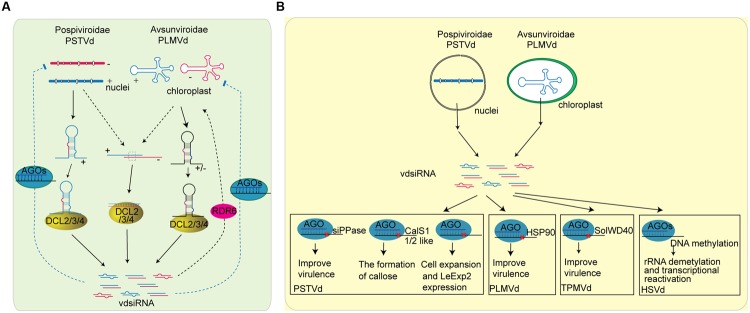
FIGURE 4.
Role of sRNAs in plant-viroid interaction. (A) The biogenesis of vdsiRNAs in plant and the possible function of vdsiRNA in plant defense to viroid. PSTVd is mainly found in nucleolus, and its vdsiRNAs predominately map to the positive strand of the left and right terminal regions. It is most likely that PSTVd-vdsiRNAs are generated from the hairpin or stem-loop structure of plus-strand of PSTV transcripts. The secondary structure of PSTVd transcripts are targeted by DCL protein and sliced into vdsiRNA. Another possible source of vdsiRNA are the accidental association of (+) and (-) strand replication, which are further target by DCL protein. On the other hand, PLMVd, viroid that replicate in the chloroplast, generate vdsiRNAs from both polarities. The stem-loop structures of PLMVd are processed by DCL protein to generate vdsiRNAs. Furthermore, some research indicate that vdsiRNAs can be amplified through the activity of RDRs. After generation, vdsiRNA may be loaded into plant AGO proteins and target viroid RNAs. (B) The function of vdsiRNAs in producing viroid symptom. Some of the viroid symptom maybe caused by vdsiRNAs that target host genes. vdsiRNA generated by PSTVd can target on various plant genes including soluble inorganic pyrophosphatase (siPPase) gene, callose synthase genes CalS11-like and CalS12-like, and LeExp2 gene, while PLMVd vdsiRNA has been reported to target HSP90 and trigger signal transduction that eventually leads to viroid disease symptoms. TPMVd vdsiRNA has also been shown to slice the SolWD40 gene. In addition, HSVd vdsiRNAs are involved in TGS by inducing DNA methylation of the promoter region of rRNA genes.