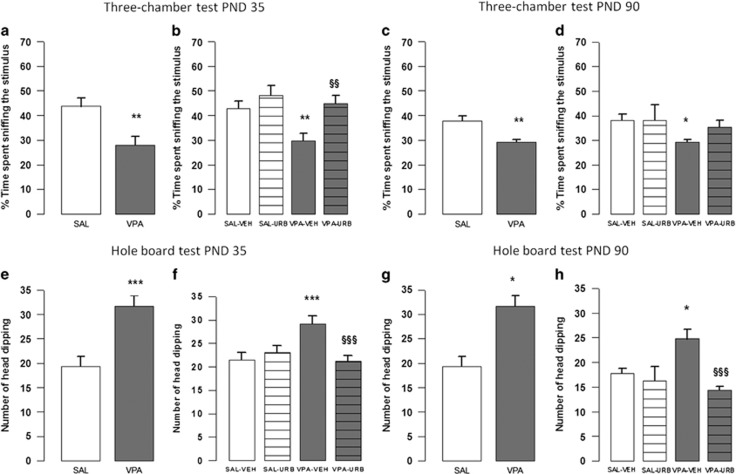
Figure 4.
Three-chamber and hole-board tests. Prenatal VPA exposure reduced sociability in the three-chamber test (a and c) at PND 35 (n (SAL)=8, n (VPA)=9) and 90 (n (SAL)=15, n (VPA)=13) and induced stereotypic behavior in the hole-board test (e and g) at PND 35 (n (SAL)=11, n (VPA)=12) and 90 (n (SAL)=12, n (VPA)=12). URB597 mitigated the altered sociability (b and d) displayed by VPA-exposed offspring at PND 35 (n (SAL-VEH)=13, n (VPA-VEH)=13, n (SAL-URB)=8, n (VPA-URB)=10) and 90 (n (SAL-VEH)=11, n (VPA-VEH)=12, n (SAL-URB)=8, n (VPA-URB)=8). Furthermore, URB597 mitigated the stereotypies (f and h) displayed by VPA-exposed offspring at PND 35 (n (SAL-VEH)=20, n (VPA-VEH)=19, n (SAL-URB)=20, n (VPA-URB)=19) and 90 (n (SAL-VEH)=8, n (VPA-VEH)=10, n (SAL-URB)=8, n (VPA-URB)=8). Data represent mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 vs SAL-VEH group; §§P<0.01, §§§P<0.01 vs VPA-VEH group (Student's t-test (a, c, e and g); Student's–Newman–Keuls post hoc test (b, d, f and h)). PND, postnatal day; SAL, saline; VEH, vehicle; VPA, valproic acid.