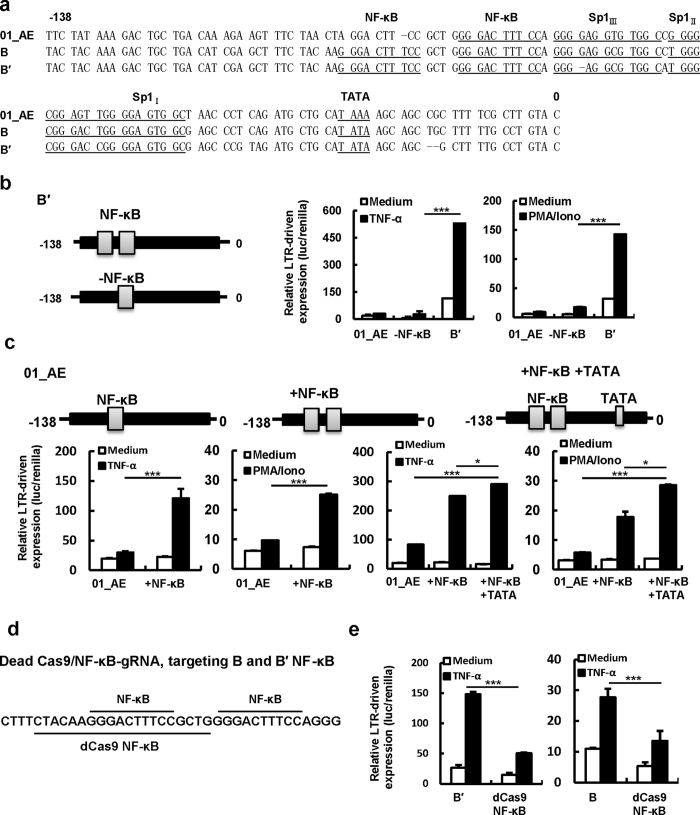
Figure 3. The frequency of NF-κB binding sites and the TATA regulatory element are essential for HIV-1-LTR activity.
(a) Alignment of the core elements in (-138-0) fragment of CRF_01AE-, B- and B′-LTR. (b,c) Assay for LTR-driven gene expression. The first NF-κB binding site was depleted from B′-LTR (−NF-κB) (b). A NF-κB binding site was added (+NF-κB), or a NF-κB binding site and the TATA box were added (+NF-κB +TATA) to 01AE-LTR (c). (d) Design of a gRNA targeting the first NF-κB binding site of B′. (e) Assay for LTR-driven gene expression. HIV-LTR-specific dCas9/gRNAs and LTR-reporter plasmids were co-transfected into HEK293T cells, and cells were harvested for quantifying LTR activity after being stimulated with TNF-α for 24 h. Data are mean ± SD. Results are representative of four independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 are considered significantly different.