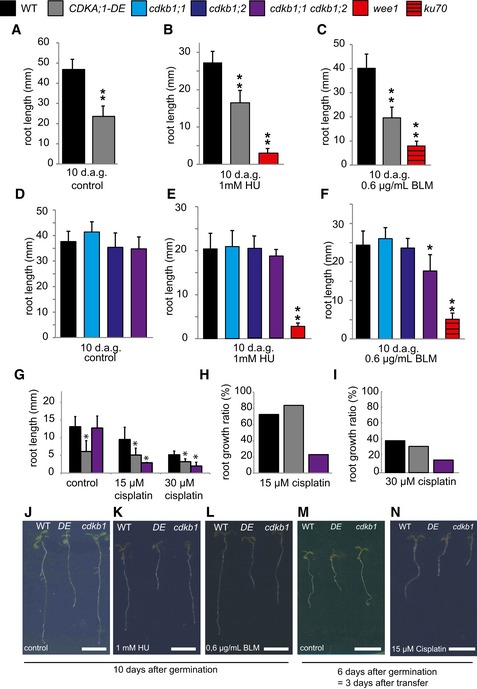
-
A–C
The wild type and CDKA;1‐DE mutants were grown on control plates (A) or containing 1 mM hydroxyurea (B) or 0.6 μg/ml bleomycin (C) for 10 days. The mutants wee1 and ku70 were used as positive controls for hydroxyurea or bleomycin sensitivity, respectively. Root lengths were measured 10 days after germination.
-
D–F
The wild type, cdkb1;1, cdkb1;2, and the double mutant cdkb1;1 cdkb1;2 were grown on control plates (D) or plates containing 1 mM hydroxyurea (E) or 0.6 μg/ml bleomycin (F) for 10 days. The mutants wee1 and ku70 were used as positive controls for hydroxyurea and bleomycin sensitivity, respectively. Root lengths were measured 10 days after germination.
-
G
The wild type, CDKA;1‐DE, and the double mutant cdkb1;1 cdkb1;2 were grown on control plates and were transferred to plates containing 15 or 30 μM cisplatin 3 days after germination. Root lengths were measured 3 days after transfer and the net root growth of 3 days is shown in the graphs.
-
H, I
Graphs represent the ratio of the mean growth rate on 15 μM (H) or 30 μM (I) cisplatin compared to control experiments on plates lacking cisplatin for the wild type, CDKA;1‐DE, and cdkb1;1 cdkb1;2.
-
J–N
Images show a wild‐type plant, CDKA;1‐DE, and the double mutant cdkb1;1 cdkb1;2 (from left to right) on the indicated day after germination and the indicated drug treatment. Scale bars: 1 cm.
Data information: One or two asterisks indicate significant differences within a 5 and 1% confidence interval, respectively (Student's
t‐test). Three biological replicates, each containing at least 15 plants, were analyzed. The mean of the root length of each individual experiment was determined and again averaged for the three biological replicates. Graphs represent mean ± SD.