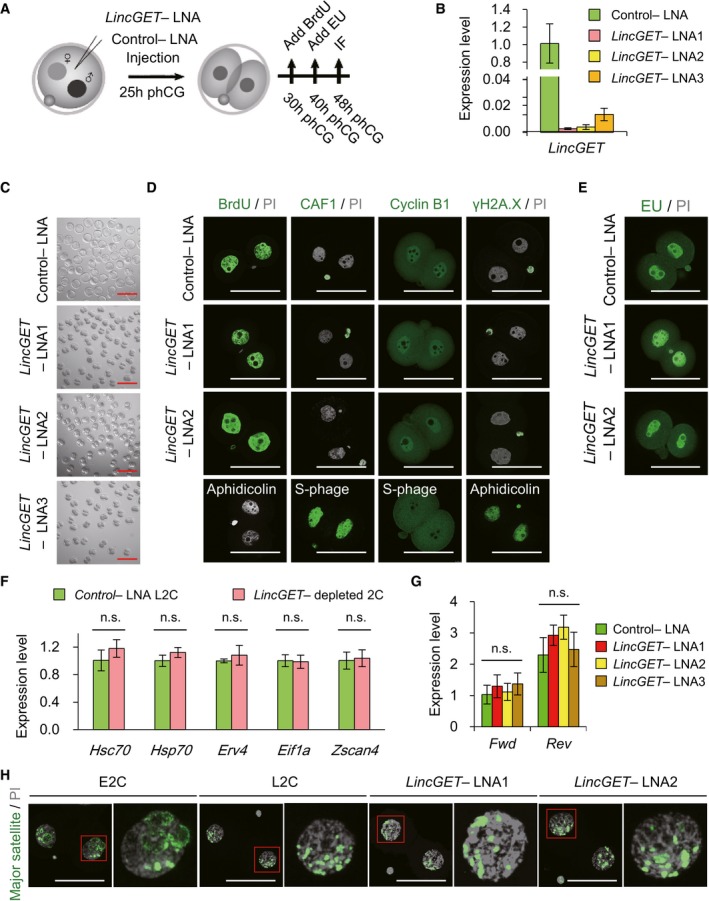
Experimental scheme to analyze the effects of LincGET depletion on embryonic development. phCG, post‐human chorionic gonadotropin injection; LNA, locked nucleic acid; IF, immunofluorescence. LNA was injected at phCG 25 h. For BrdU staining, BrdU was added at phCG 30 h. For EU staining, EU was added at phCG 40 h. IF, including detection of BrdU and EU, was performed at phCG 48 h.
LNA efficiently mediated LincGET knockdown. LNA was injected at phCG 25 h, and embryos were collected at phCG 48 h at late two‐cell stage for TM‐qPCR analysis. The error bars represent s.e.m. About 50 embryos of each stage were used, and three experimental replicates were performed.
LincGET‐depleted embryos arrest at the two‐cell stage. LNA was injected at phCG 25 h, and photographs were taken at phCG 114 h at the late blastocyst stage. Embryos injected with control‐LNA can develop to the late blastocyst stage, while
LincGET‐depleted embryos arrest at the two‐cell stage. Scale bar, 100 μm. At least three experimental replicates were performed for each LNA injection (Table
1).
LincGET depletion results in developmental arrest at the G2 phase of two‐cell stage without affecting DNA integrity and replication. We used BrdU to visualize S and G2 phases, CAF‐1 to visualize S phase, and PI to visualize the M phase. Cyclin B1 is a marker of G2 stage, and H2A.X is a marker of DNA damage. Aphidicolin‐treated embryos arrest at the S phase without DNA replication. LNA was injected at phCG 25 h, and embryos were collected at phCG 48 h at the late two‐cell stage for IF analysis. Scale bar, 50 μm. Three experimental replicates were performed, and about 15 embryos were used in each group.
EU staining indicates the normal major ZGA process after LincGET depletion. EU was added to the culture medium at phCG 40 h, and EU signals were detected at phCG 48 h. Scale bar, 50 μm. Three experimental replicates were performed, and about 15 embryos were used in each group.
Genes related to major ZGA initiation, like Hsc70, Hsp70, Erv4, Eif1a, and Zscan4, are expressed normally in LincGET‐depleted L2C embryos compared to that in control embryos. Embryos injected with LNA were collected at phCG 48 h at the late two‐cell stage for TM‐qPCR analysis. The error bars represent s.e.m. About 100 embryos were used for each group, and three experimental replicates were performed. n.s., P > 0.05.
The transcription of pericentric satellites is normal after LincGET depletion. Embryos injected with LNA were collected at phCG 50 h at the late two‐cell stage for TM‐qPCR analysis. The error bars represent s.e.m. About 50 embryos were used for each group, and three experimental replicates were performed. n.s., P > 0.05.
DNA‐FISH analysis of major transcripts shows that the pericentric domain reorganization toward chromocenters is not affected by LincGET depletion. Scale bar, 50 μm. Three experimental replicates were performed, and about 15 embryos were used in each group.