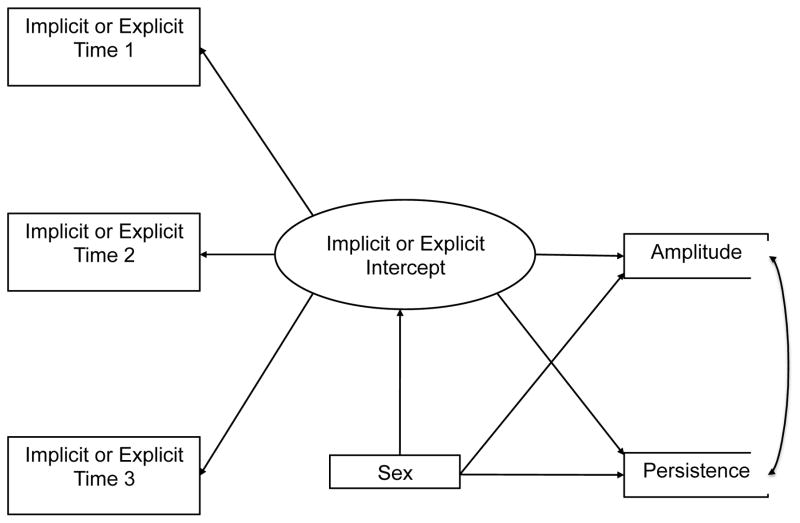
Figure 1.
Illustration of individual models. Four separate models fit either implicit or explicit measures of drinking identity or alcohol-approach inclinations to predict both Amplitude and Persistence. Implicit and explicit measures of drinking identity and alcohol approach inclinations were assessed at three timepoints separated by three-month intervals. Given no evidence of growth over time, random intercept-only models (i.e., intercept reflects the composite score in a measure across the three timepoints) were used to predict Amplitude and Persistence. All models included sex, which was dummy-coded (0 = men, 1 = women).