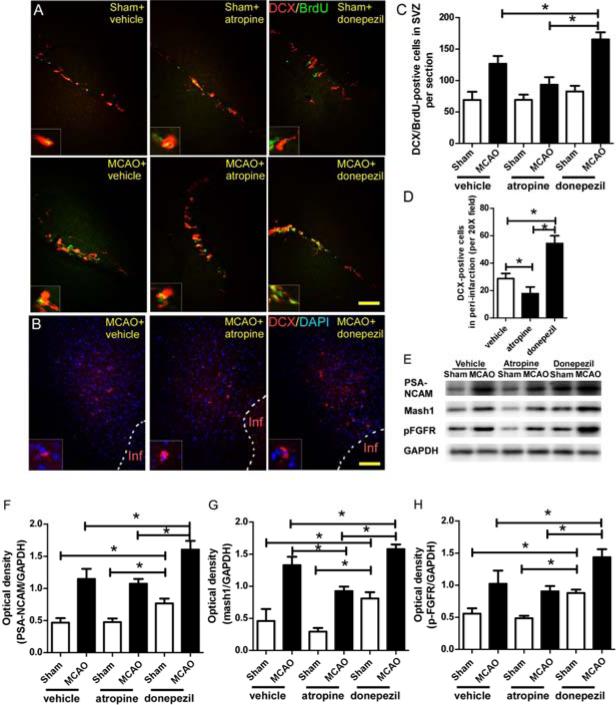
Figure 3.
The cholinergic system (ChAT+ neurons) participates in post-stroke neurogenesis. (A) Immunofluorescence staining of BrdU and DCX in the SVZ of mice on day 7 after MCAO. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of DCX in the peri-infarction region of mice on day 7 after MCAO. (C and D) Quantification showed that activation of the cholinergic system by donepezil significantly increased the number of BrdU/DCX+ cells in the SVZ and the number of DCX+ cells in the peri-infarction region compared with the corresponding numbers in the vehicle-treated MCAO mice; inhibition of mAchRs by atropine significantly reversed these effects. *p<0.05, n=8/group. Values are mean ± SD. (E) Western blot analysis of PSA-NCAM, mash1, and p-FGFR in SVZ on day 7 after MCAO. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (F-H) Quantification of band densities showed that vehicle-treated MCAO mice had higher levels of PSA-NCAM, mash1, and p-FGFR in SVZ than did the sham+vehicle group. Donepezil significantly enhanced this neurogenic effect. Atropine significantly decreased the mash1 level in the SVZ of MCAO mice compared to that of the MCAO+vehicle group. In the sham groups, donepezil also increased the levels of PSA-NCAM, mash1, and p-FGFR compared with levels in the other two sham groups. *p<0.05, n=8/group. Values are mean ± SD.