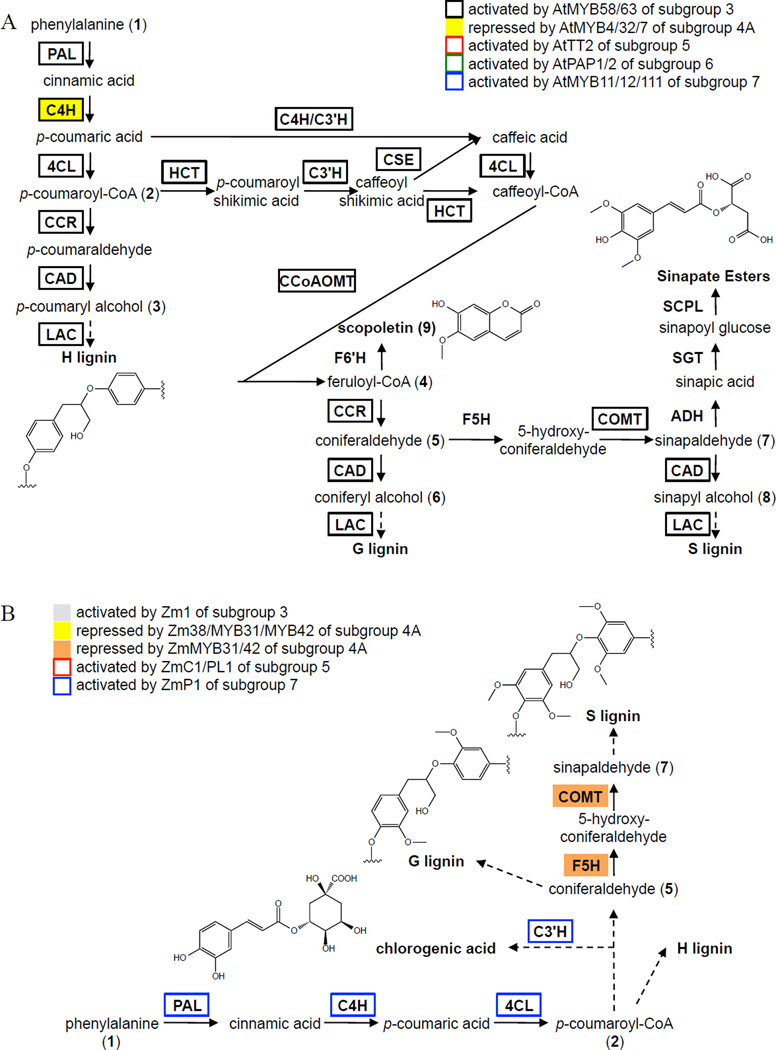
Figure 2. Multiple R2R3-type MYB Subgroups Regulate the Lignin Biosynthetic Pathways in Arabidopsis and Maize.
Unbroken arrows indicate single enzymatic conversions, and broken arrows indicate multiple enzymatic conversions. (A) Arabidopsis lignin pathways. Adapted from Vanholme et al. (2010, 2013). (B) Maize lignin pathways. Feruloyl-CoA (4) is at the intersection of the G/S lignin and coumarin biosynthetic pathways. Sinapaldehyde (16) is at the intersection of the sinapate ester and S lignin biosynthetic pathways. Monolignols, p-coumaryl (3), coniferyl (6), and sinapyl (8) alcohols, polymerize to form H, G and S lignin, respectively. ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; C3’H, p-coumaroyl ester 3’-hydroxylase; C4H; cinnamate 4-hydroxylase; CAD, cinnamoyl-alcohol dehydrogenase; 4CL, 4-coumarate:CoA ligase; CCoAOMT, caffeoyl-CoA O-methyltransferase; CCR, cinnamoyl-CoA reductase; COMT, caffeic acid O-methyltransferase; CSE, caffeoyl shikimate esterase; F5H, ferulate 5-hydroxylase; F6’H, feruloyl-CoA 6’-hydroxylase; HCT, hydroxycinnamoyl-CoA:shikimate/quinate hydroxycinnamoyltransferase; LAC, laccase; PAL, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase; SCPL, serine carboxypeptidase-like; SGT, sinapate UDP-glucose sinapoyltransferase.