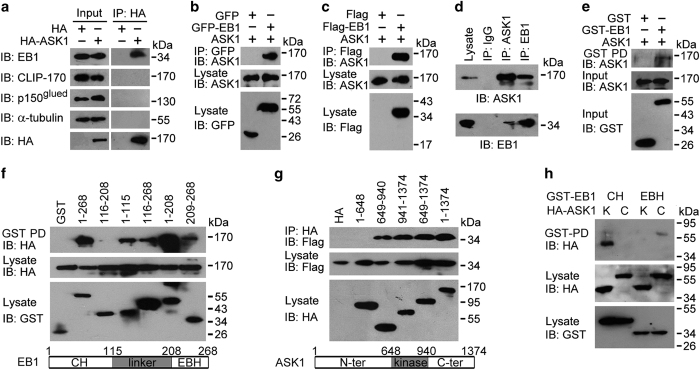
Figure 4.
ASK1 interacts with EB1 both in cells and in vitro. (a) Immunoprecipitation (IP) and immunoblotting (IB) showing that HA-ASK1 interacts with endogenous EB1, but not CLIP-170, p150glued, or α-tubulin in 293 T cells. (b–d) Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting showing that endogenous ASK1 interacts with GFP-EB1 (b), Flag-EB1 (c) and endogenous EB1 (d) in 293 T cells. (e) GST pulldown (PD) and immunblotting showing that in vitro-translated ASK1 interacts with bacterially purified GST-EB1, but not GST. (f, g) Characterization of the domains mediating the interaction between ASK1 and EB1 in cells transfected with HA-ASK1 and different forms of EB1 tagged with GST (f), or Flag-EB1 and different forms of ASK1 tagged with HA (g). Schematic diagrams of the CH domain, linker region and EBH domain of EB1 (f), and the N-terminal region, kinase domain and C-terminal region of ASK1 (g) are shown below the blots. (h) GST pulldown and immunblotting showing that the CH domain of EB1 interacts with the kinase (K) domain of ASK1 and that the EBH domain of EB1 interacts with the C-terminal (C) region of ASK1 in 293 T cells.