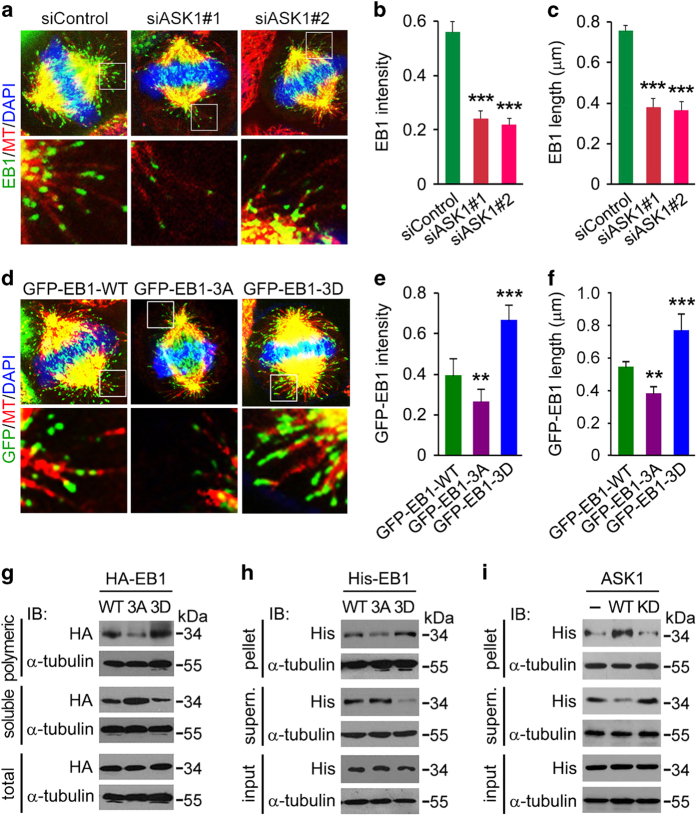
Figure 7.
EB1 phosphorylation enhances its binding to the plus ends of astral microtubules. (a–c) Immunofluorescence images (a), intensity (b) and length (c) of EB1 at the plus ends of astral microtubules in metaphase HeLa cells transfected with control or ASK1 siRNAs and stained with DAPI and antibodies against α-tubulin and EB1. The intensity and length of EB1 comets were analyzed with Image J. n=100 comets from 10 cells. (d–f) Immunofluorescence images (d), intensity (e) and length (f) of GFP-EB1 at the plus ends of astral microtubules in metaphase HeLa cells transfected with EB1 siRNA and GFP-EB1-WT, -3A or -3D and stained with anti-α-tubulin antibody and DAPI. The intensity and length of EB1 comets were analyzed with Image J. n=100 comets from 10 cells. (g) 293 T cells were transfected with HA-EB1-WT, -3A or -3D. Cell extracts containing polymeric and soluble tubulin fractions were then prepared and analyzed by immunoblotting. Please see ‘Materials and Methods’ for experimental details. (h) Bacterially purified His-EB1-WT, -3A or -3D was incubated with preassembled microtubules for 30 min. Microtubules were then pelleted by centrifugation, and proteins in the pellet and supernatant fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting. Please see ‘Materials and Methods’ for experimental details. (i) Kinase assays were performed by using ASK1 or ASK1KD immunoprecipitate from 293 T cells, with bacterially purified His-EB1 as a substrate. His-EB1 pulled down from the above mixture was then incubated with preassembled microtubules for 30 min. Microtubules were then pelleted by centrifugation, and proteins in the pellet and supernatant fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting. Please see ‘Materials and Methods’ for experimental details. Experiments were performed three times. Values are mean±s.e.m. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.