Figure 2.
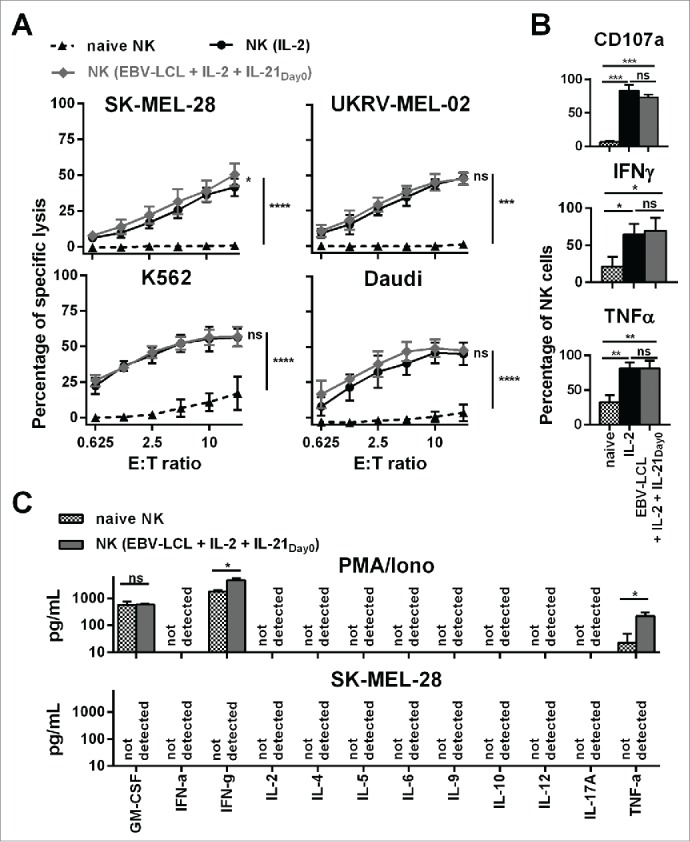
Ex vivo-expanded NK cells were highly cytotoxic against different tumor cell lines and showed enhanced degranulation and production of IFNγ and TNF-α. (A) Different NK cells were tested for cytotoxicity against four tumor cell lines using a standard 51Chromium release assay. Specific lysis at different effector-to-target (E:T) ratios is shown for freshly isolated NK cells (black triangles and dashed line) and NK cells that have been expanded for 13 or 14 d, either with IL-2 (back line and dots) or by use of IL-2, irradiated EBV-LCL and IL-21 supplemented at day 0 (gray line and diamonds). Displayed are mean values and standard deviation of NK cells from 4–8 donors per target cell line and statistical significance was tested by Student's t-test. (B) NK cells were tested for degranulation and production of IFNγ and TNF-α by flow cytometry upon stimulation with PMA/Iono. Shown are data for freshly isolated, naive NK cells (gray and white dotted bars) and NK cells that have been expanded for 13 or 14 d, either with IL-2 (black bars) or by use of IL-2, irradiated EBV-LCL and IL-21 supplementation at day 0 (gray bars). Displayed are mean values and standard deviation of NK cells from five donors. Statistical significance was tested by paired Student's t-test. (C) NK cells were expanded ex vivo for 14 d by use of IL-2, irradiated EBV-LCL and IL-21 supplementation at day 0. Then, NK cells were stimulated for 24 h with PMA/Iono or by co-culture with SK-MEL-28 cells. Supernatants of the cell cultures were harvested and analyzed for the concentrations of 12 different cytokines using a multiplex bead-array assay. Mean and standard deviation for NK cells from three different donors are displayed. Statistical significance was tested by paired Student's t-test.
