Figure 2.
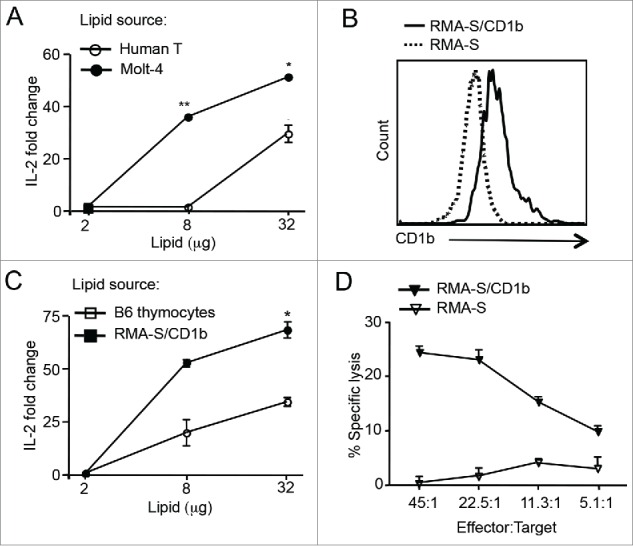
HJ1 T cells can recognize tumor-derived lipids and kill CD1b-expressing RMA-S T cell lymphoma. (A) Extracted lipids from PBMC-derived human T cells (open circle) and Molt-4 cells (black circle) were loaded on to purified CD1b protein and subsequently incubated with 5 × 104 HJ1 T cell hybridoma cells. Twenty-four hours later, IL-2 in the supernatant was measured by ELISA. HJ1 incubated with CD1b without added antigens had a value of 1 and fold change was calculated using this value as reference. (B) Surface expression of CD1b on RMA-S cells and RMA-S/CD1b transfectants was determined by flow cytometry. RMA-S/CD1b transfectants stained with anti-CD1b antibody are depicted by the black line. RMA-S cell stained with anti-CD1b antibody are represented by the dotted line. (C) Extracted lipids from B6 thymocytes (open square) and RMA-S/CD1b cells (black square) were used to stimulate HJ1 T cell hybridoma as in (A). (D) HJ1 CTL effectors were incubated at different ratios with 51Cr labeled RMA-S (open triangle) or RMA-S/CD1b (black triangle) targets for 4 h. Supernatant was collected and assayed for the presence of 51Cr. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments. Error bars represent the mean ± SEM. ***p < 0.005; **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05.
