Fig. 2.
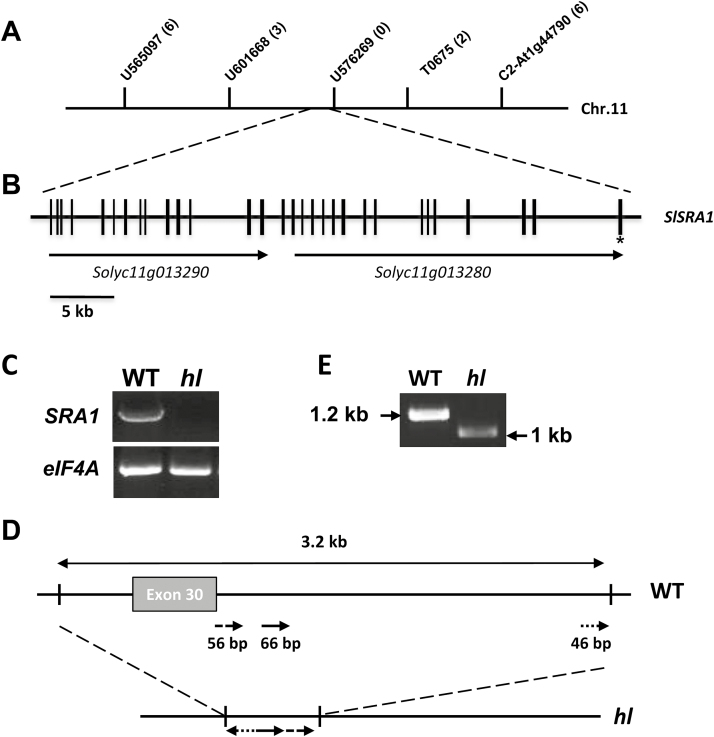
The Hl gene encodes the tomato homolog of SRA1. (A) Fine genetic mapping of Hl delimited the target gene to an interval between marker U601668 and T0675 on tomato chromosome 11. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of recombination events identified between markers and the target gene. (B) Structure of SlSRA1. Vertical black lines depict exons and horizontal lines indicate intervening introns or intergenic regions. The mutation identified in the hl mutant affects the last exon, denoted with an asterisk. The relative location and direction of transcription of annotated genes (Solyc11g013290 and Solyc11g013280) is shown. (C) Agarose gel showing the results of RT-PCR amplification of SRA1 cDNAs using mRNA isolated from WT and hl leaves. Elongation factor 4A (elF4A) mRNA was used as a loading control. (D) Diagram depicting the nature of the deletion mutation identified in the hl mutant, as compared to the same genomic region of the WT. The hl mutation corresponds to a 3.2-kb deletion spanning the last exon of the gene. Arrows depict the directionality of short segments of DNA that are retained in the mutant. (E) Agarose gel showing the amplification products from 3ʹRACE of the SRA1 cDNA, using mRNA isolated from WT and hl leaves.