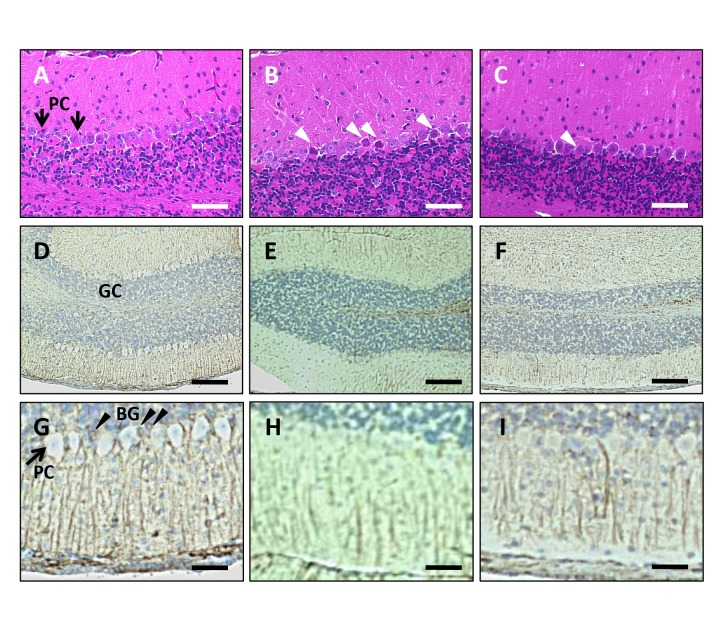
Fig. 3.
Histological analyses of the cerebellum.
(A–C) HE staining of the cerebellum. Bar = 100 μm. (A) The cerebellum from NR mice. Arrows indicate Purkinje cells (PC). (B) VEdef mouse cerebellum shows neuronal degeneration of Purkinje cells (white arrow heads). (C) Addition of 5%RB inhibits the neuronal degeneration of Purkinje cells. Neurodegeneration (white arrow head) is reduced compared to that in VEdef mice. (D–I) Immunohistochemistry using anti-GFAP antibody. (D–F) Low magnification. Bar = 200 μm. (G–I) High magnification. Bar = 50 μm. GC: Granule cell layer. PC: Purkinje cells. BG: Bergmann glia. (D and G) GFAP positive Bergmann glia (black arrow heads) are observed around Purkinje cells. (E and H) GFAP immunoreactivity in Bergmann glia is reduced in the cerebellum of VEdef mice compared to NR or RB5% mice. (F and I) The GFAP immunoreactivity of Bergmann glia is recovered by 5%RB supplementation. GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; HE, hematoxylin-eosin; NR, normal diet alone; RB, rice bran; 5%RB, a mixture of vitamin E deficient feed and RB at a concentration 5% rice bran; VE, vitamin E; VEdef, vitamin E-deficient feed.