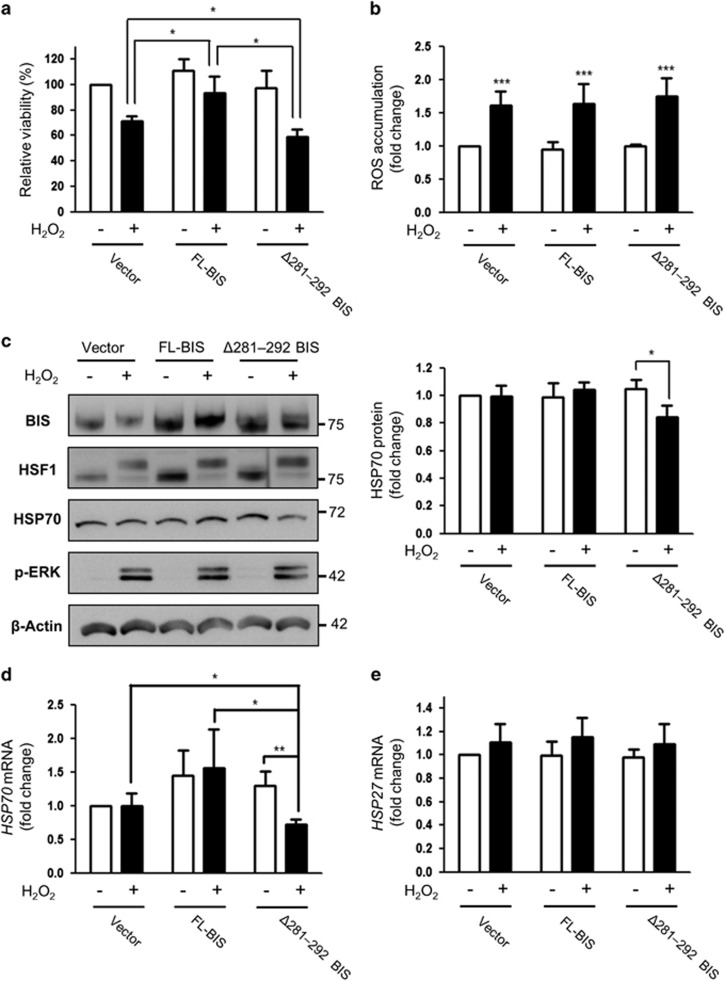
Figure 4.
Effect of Δ281–292 BIS overexpression on cell viability and HSP70 expression following H2O2 treatment. A172 cells were transfected with pCAGGS (Vector), FL-BIS, or Δ281–292 BIS and then treated 48 h later with 100 μM H2O2 for 3 h. (a) Cell viability was determined with the water soluble tetrazolium salt assay; viability of cells transfected with the empty vector was designated as 100%. Values represent the mean±s.e. of triplicate experiments. *P<0.05. (b) Intracellular ROS levels were assessed by CM-H2DCFDA staining and flow cytometry. Data are presented as the fold change in the mean value from three independent experiments with the s.e. ***P<0.001 vs untreated cells (c) Expression levels of BIS, HSP70, HSF1, and p-ERK were determined by western blotting (left panels). The results from a densitometric analysis of HSP70 protein levels from three independent experiments are shown in the right panels. The basal level of HSP70 protein in A172 cells transfected with the vector was arbitrarily set to 1. Relative levels of (d) HSP70 mRNA and (e) HSP27 mRNA were evaluated by quantitative real-time PCR. Values represent the mean±s.e. of triplicate experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. BIS, B-cell lymphoma (BCL)-2-interacting cell death suppressor; ERK, extracellular signaling-regulated kinase; HSF1, heat shock transcription factor 1; HSP70, heat shock protein 70; ROS, reactive oxygen species.