Figure 1.
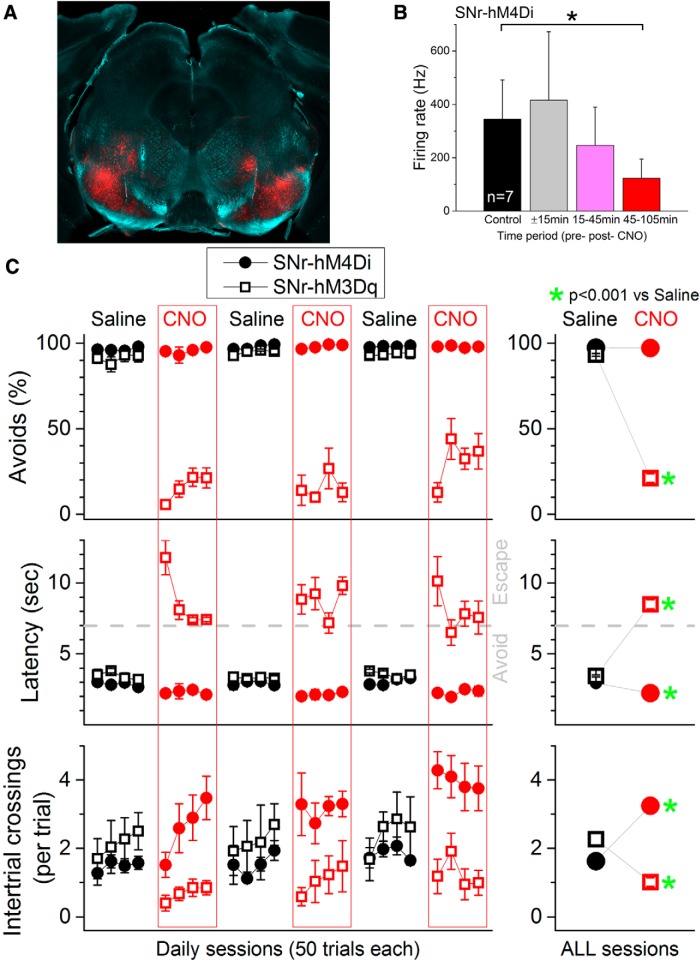
Effects of DREADDs in SNr on active avoidance. A, Photomicrograph showing mCherry fluorescence in the SNr of an SNr-hM3Dq mouse. Image blends a dark-field image of the section with the red channel of the fluorescent image. B, CNO (20 mg/kg, i.p.) inhibits the spontaneous firing of SNr cells in SNr-hM4Di mice. Population data showing the firing rate from SNr recordings (single units and multiunits are combined; n = 7) during a control period (30 min), 15 min before and immediately after CNO, and 2 periods thereafter. CNO significantly suppressed SNr firing 45–125 min after CNO, which is the period during which CNO is tested on active avoidance. C, CNO blocks active avoidance in SNr-hM3Dq mice (n = 5) and facilitates active avoidance in SNr-hM4Di mice (n = 6). Percentage of avoidances (Avoids), latency from ACS onset, and number of intertrial crossings for all daily active avoidance sessions in which mice were injected with either saline (black) or CNO (red). The right panels combine the data for all the daily sessions and highlight statistical differences.