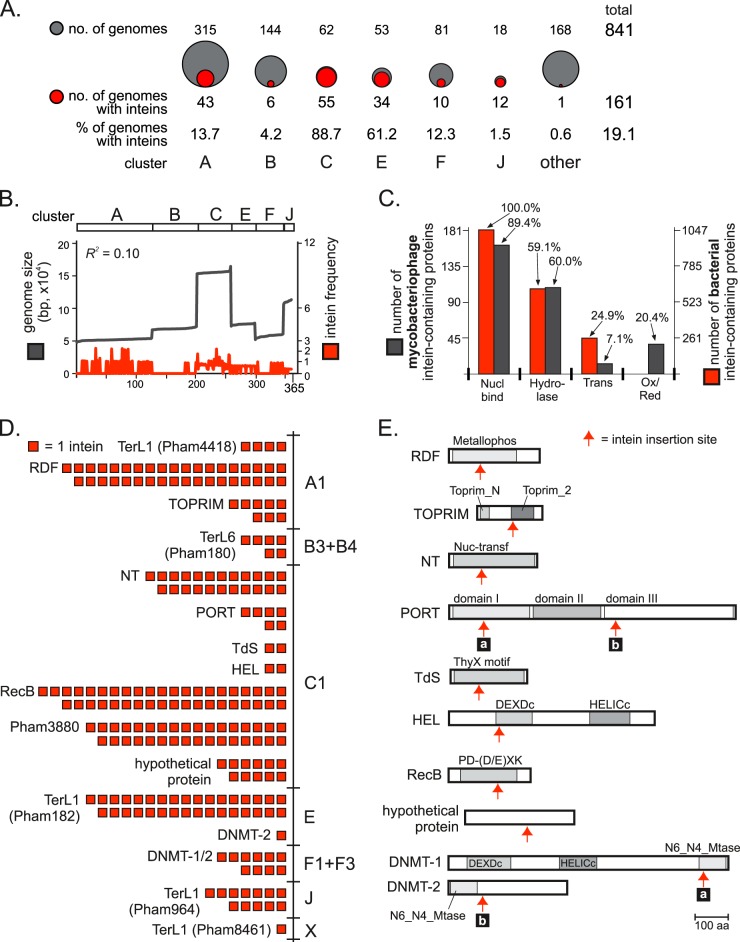
FIG 1 .
Overview of intein distribution in mycobacteriophages. (A) Distribution of inteins among mycobacteriophage clusters. The number of intein-positive genomes (red, value below the circle) was compared to the total number of sequenced phage genomes (gray, value above the circle) in a cluster. “Other” includes clusters D, G to I, K to Z, and singletons. (B) Distribution of inteins does not correlate with genome size. Vertical axis represents genome sizes (black) and frequency of inteins (red; number of inteins per 100 protein-coding sequences) in corresponding phages on the horizontal axis. Mycobacteriophage genomes (365 had protein-coding sequence numbers available) are organized by cluster. Coefficient of determination, R2 = 0.10. (C) Functional genomics of intein-containing proteins. Results for Gene Ontology (GO) term enrichment analysis of dominant functional categories of mycobacteriophage proteins with inteins are compared to those for bacterial intein-containing proteins. GO term enrichment of the 181 mycobacteriophages which gave GO terms (red) and 1,047 bacterial (gray) intein-containing proteins, previously analyzed (5). Dominant GO terms are shown: Nucl bind, nucleotide binding (GO:0003676); hydrolase (GO:0016787); Trans, transferase (GO:0016740); and Ox/Red, oxidoreductase (GO:0016491). The percentages of the associated proteins are indicated above the bars. (D) Intein distribution by host protein and phage clusters. Each square represents one intein. (E) An overview of intein-containing proteins indicates the intein insertion site relative to protein domains (arrow). Intein insertion sites for TerL and Pham3880 are shown in Fig. 2A. Abbreviations: TerL1, large terminase subunit terminase_1; TerL6, terminase_6; Pham3880, terminase-like; RDF, recombination directionality factor; TOPRIM, topoisomerase-primase; NT, DNA nucleotidyltransferase; PORT, portal protein; TdS, thymidylate synthase; HEL, helicase; RecB, RecB-like exonuclease; DNMT-1/2, DNA methyltransferase; Metallophos, metallophosphoesterase domain; Nuc-transf, nucleotidyltransferase domain; DEXDc and HELICc, domains associated with DEAD-like helicases; PD-(D/E)XK, nuclease domain; N6_N4_Mtase, DNA methylase; aa, amino acids.