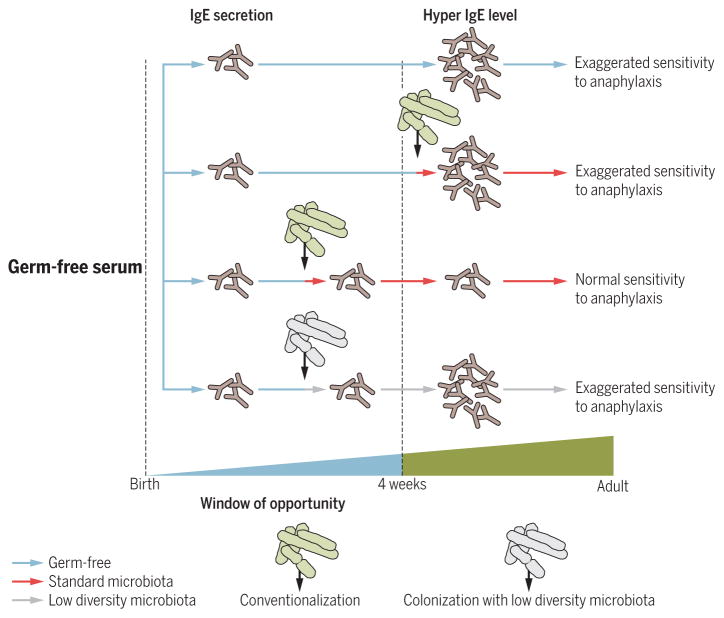
Fig. 2. Exposure to a microbiota during early life regulates IgE levels in serum of adult mice and their sensitivity to orally induced anaphylaxis.
IgE accumulates in the serum of GF mice 4 weeks after birth because of an isotype switch to IgE in mucosal B cells. “Hyper-IgE levels” lead to an exaggerated sensitivity to orally induced anaphylaxis that can be resolved through conventionalization with a standard microbiota during early life but not thereafter. Colonization of GF mice with low-diversity microbiota during the window of opportunity fails to normalize hyper-IgE levels in adult life.