Figure 3. A schema showing the effects of ROS and other mediators on HSCs during liver injury.
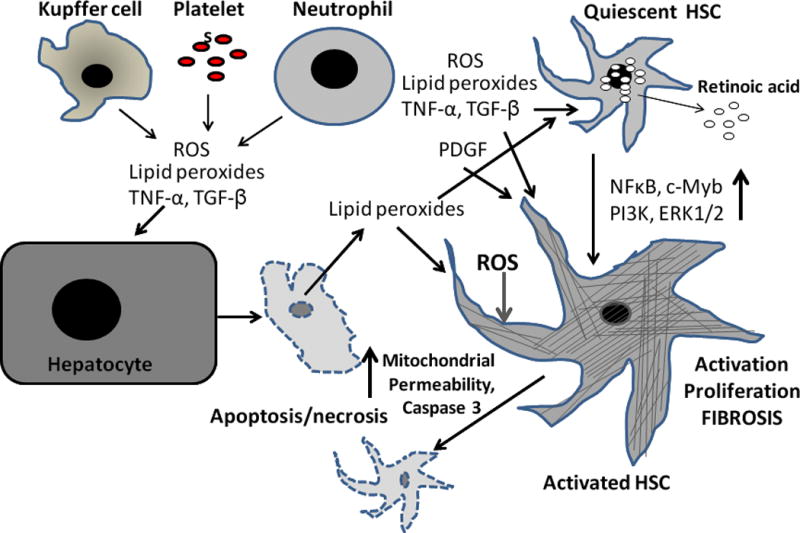
Upon liver injury (e.g., CCl4 administration), Kupffer cells, platelets and infiltrating blood cells such as monocytes and neutrophils produce several mediators including ROS and lipid peroxides. CCl4 also causes hepatocyte apoptosis/necrosis, which release several mediators, including ROS and lipid peroxides. These mediators act on quiescent HSCs, which release retinoids and change their phenotype to myofibroblast-like cells. While these mediators continue to induce HSC activation, and also proliferation of activated HSCs and promote their fibrogenic activity, a subpopulation can undergo apoptosis in response to ROS challenge. NFkB, c-Myb, PI3K and ERK1/2 have been shown to participate in activation/proliferation of HSCs. See text for details.
