Fig. 1.
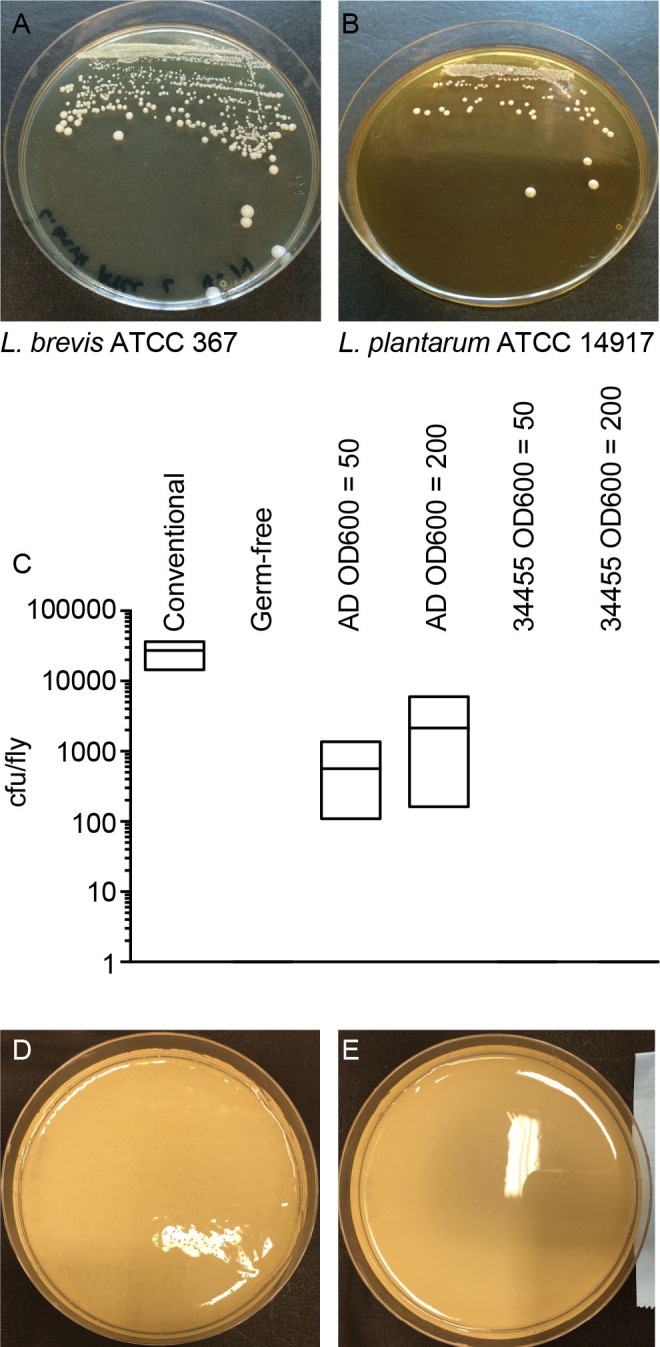
Evaluation of bacterial strain survival. (A,B) Homogenates from gnotobiotic flies mono-associated with L. brevis ATCC 367 (A) and L. plantarum ATCC 14917 (B), 10 days after the initial feeding. Each plate contains the equivalent of 1% of the homogenate of an entire fly. (C) Quantification of A. pasteurianus association with conventionally reared (column 1) flies, germ-free (column 2) flies, gnotobiotic flies that were fed A. pasteurianus strain AD at OD600 of 50 and 200, respectively (columns 3 and 4), or gnotobiotic flies that were fed A. pasteurianus strain ATCC 33445 at OD600 of 50 and 200, respectively (columns 5 and 6). Each column shows the results of three separate measurements, and association was measure as bacterial colony-forming units per fly. (D, E) Liquid cultures A. pasteurianus AD (D) and A. pasteurianus ATCC 33445 (E) were added to fly food, incubated at 29°C for 1 week, rinsed in MRS and re-plated on selective plates.
