Fig. 4.
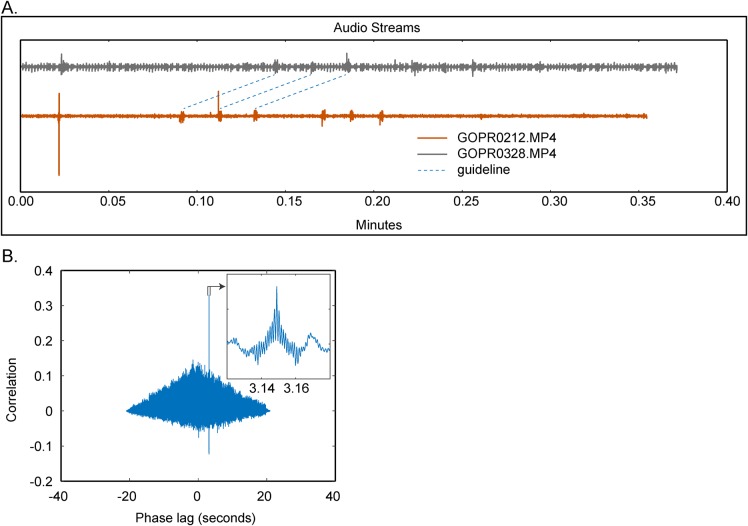
Argus uses cross-correlation of audio streams from the different camera files to determine the camera synchronization offset. (A) Argus Sync screenshot displaying two audio streams which include six distinct calibration tones as well as substantial background noise which makes the synchronization offset difficult to determine visually. The blue dashed guidelines, added to the figure and not present in Argus, highlight the calibration tones and span ∼0.05 min (∼3 s). (B) Results of a cross-correlation among the two audio streams; although background noise makes the offset difficult to determine by eye, the cross-correlation identifies a distinct positive peak at ∼3.15 s; this is the actual synchronization offset between the two cameras. The cross-correlation operations are performed within Argus Sync and processed automatically; results are saved in a user-specified text file.