Fig. 2.
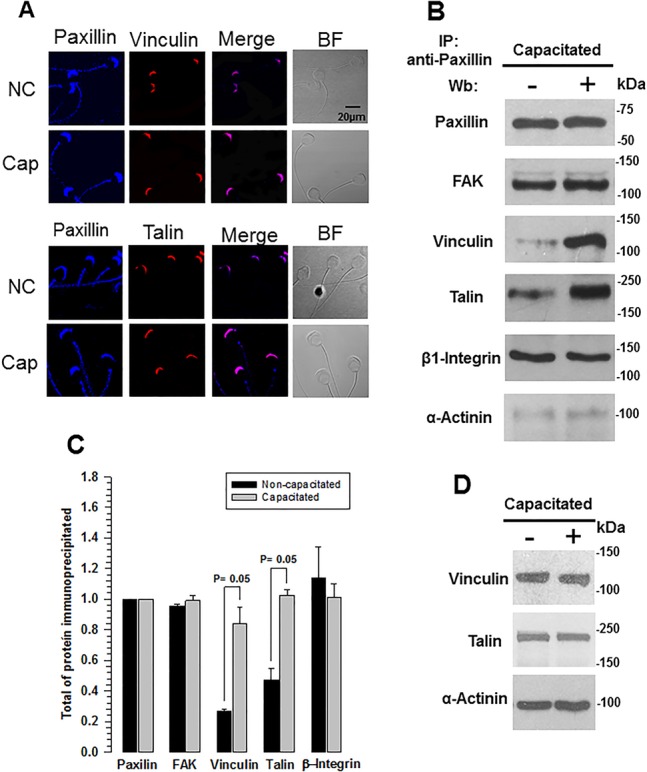
Talin and vinculin are associated with the focal adhesion complex during capacitation. (A) To determine the changes undergone by vinculin and talin in the focal adhesion complex, co-localization of vinculin and talin (red) with paxillin (blue) was visualized by immunocytochemical assays in formaldehyde-fixed non-capacitated (NC) and capacitated (Cap) guinea pig spermatozoa. The merged (pink) and bright field (BF) images are also shown. Images are representative of three independent experiments. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation assays of paxillin with the focal adhesion proteins were performed to determine changes in the complex. Total sperm extracts were immunoprecipitated from non-capacitated and capacitated guinea pig spermatozoa using the anti-paxillin antibody. The precipitated proteins were subject to SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis was performed using anti-paxillin, anti-FAK, anti-β-integrin, anti-vinculin, anti-talin, and anti-α-actinin antibodies. The image is representative of five independent experiments. (C) Densitometric analysis of co-immunoprecipitated focal adhesion proteins. The results are expressed as the ratio N/No, where N is the total amount of each co-immunoprecipitated protein and No is the total amount of paxillin immunoprecipitated (mean±s.e.m., n=3 independent experiments). (D) Western blot showing that the amount of vinculin, talin, and α-actinin did not change during capacitation. Images are representative of three independent experiments.
