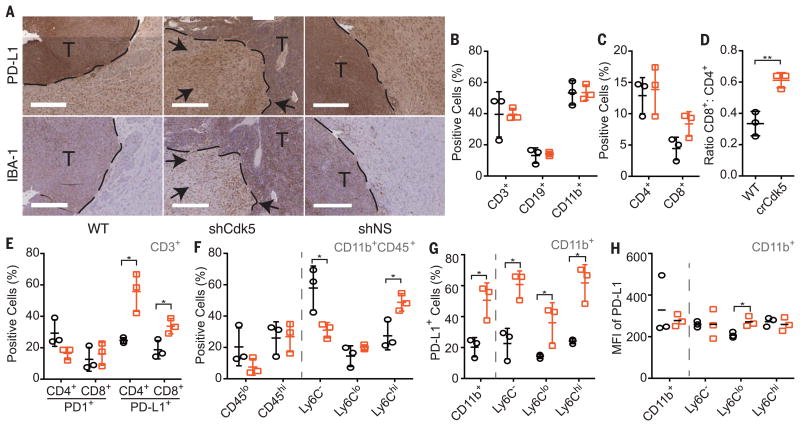
Fig. 4. Orthotopic Cdk5-deficient tumors exhibit increased PD-L1 staining, CD4+ tumor–infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), and accumulating infiltrates of CD11b+ populations.
(A) Tumors extracted 14 days postinoculation from MM1 WT, shCdk5, or shNS mice stained for PD-L1 expression. Dashed line represents margin between tumor (T) and stroma. Black arrows point to increased PD-L1+ and IBA-1+ cells in the tumor stroma. Scale bars, 400 μm. (B and C) Fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) analysis of MM1 WT (black circle) and MM1 crCdk5 (orange square) tumor infiltrate by percentage of cell type. (D) Ratio of total CD8+:CD4+ cell infiltrate. (E) FACS analysis of the percentage of PD-1+ or PD-L1+ cells in the CD4+ or CD8+ populations. (F) FACS analysis of the percentage of myeloid cells in tumor infiltrate based on differential CD45 staining (left) or Ly6C staining among CD11b+CD45+ cells (right). (G) Percent of total CD11b+ population (left) and subpopulations (right) present in tumor infiltrate that express PD-L1. (H) MFI of PD-L1 expression among CD11b+ total population (left) and subpopulations (right). (B), (C), (D), (E), (F), and (G) were graphed as means ± SD. (H) was graphed as individual MFI with mean indicated. n = 9 per group. Each data point represents pooled samples from three mice. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Significance was determined using the Student's t test.