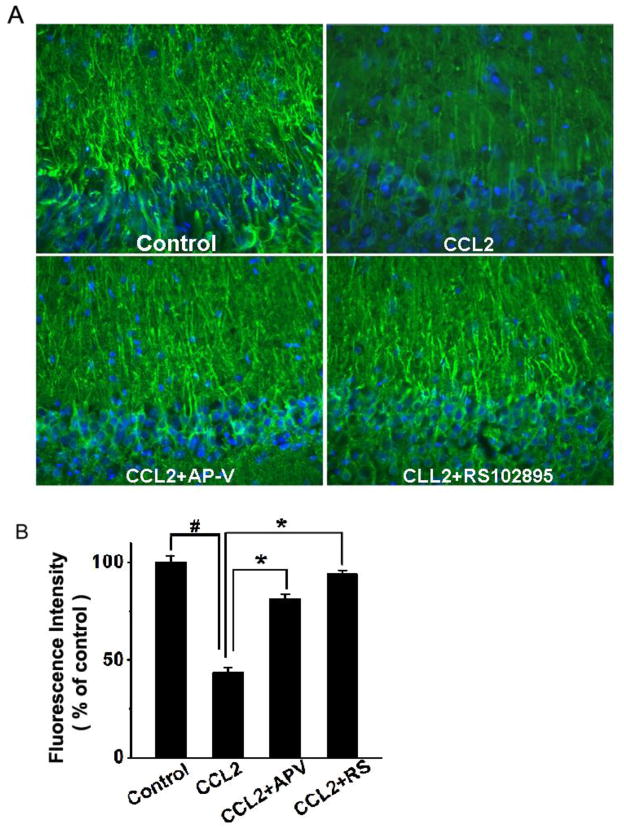
Figure 5. Attenuation of CCL2-induced dendritic injury in the CA1 region of hippocampal slices as revealed by MAP-2 staining.
Panel A shows the representative sections of the CA1 region immunostained with antibodies to MAP-2 in different experimental conditions as indicated. The same region of the CA1 was selected in all samples. MAP-2 expression was reduced in the CCL2-treated group (CCL2) as compared with the untreated group (control). The CCL2-induced reduction of MAP-2 expression was attenuated by either a NMDA receptor antagonist AP-V (CCL2+AP-V), or a CCR2 receptor antagonist RS102895 (CCL2+RS102895), demonstrating that CCL2 induces dendritic injury via NMDA receptor and CCR2 receptor which are expressed in the hippocampus. Quantification of fluorescence intensities using ImageJ software is shown in panel B. Note that CCL2 significantly reduced the fluorescence intensity and such a reduction was significantly attenuated by AP-V (CCL2+AP-V) or RS102895 (CCL2+RS). Values are expressed as mean±SE from five independent experiments. # p< 0.05 vs control, * p < 0.05 vs CCL2 group. Objective magnification: 20×