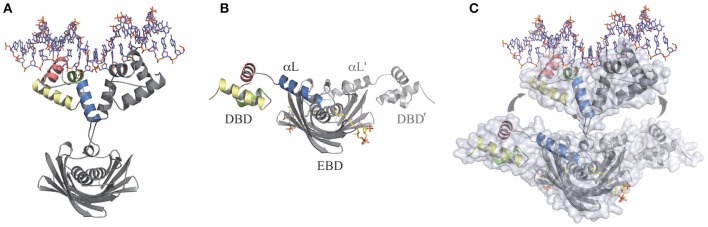
Figure 2.
The transitional switch between the relaxed and tense states of FapR involves a significant structural rearrangement of the DBDs. (A) Relaxed state: FapR in complex with DNA in which the amphipathic linker α-helix (αL) from each protomer associates with each other. (B) Tense state: FapR in complex with malonyl-CoA (shown in stick representation). (C) Superposition of the two conformational states of the repressor illustrating the structural transition which involves substantial changes and large (~30 Å) inter-domain movements. Solvent accessible surfaces are shown in transparent to highlight the DNA-induced dissociation of the invariant effector-binding domain (EBD) from the DNA-binding domains (DBDs). The molecules are shown in light (relaxed) and dark (tense) gray, except for the helices from one DBD (colored). Adapted from Albanesi et al. (2013).