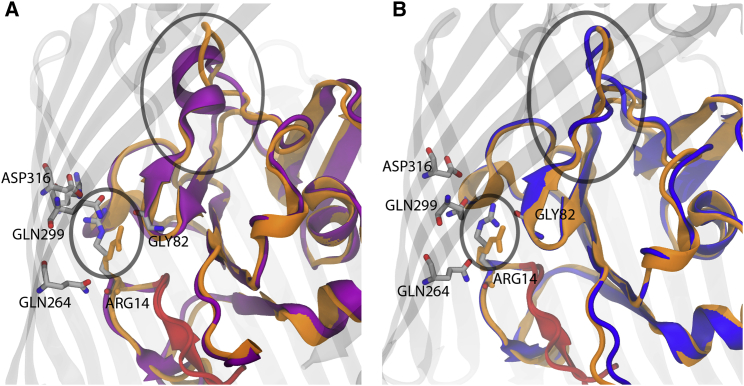
Figure 4.
(A and B) Luminal domain organization of the (A) Apo-sym (purple ribbon) and (B) Apo-OM (blue ribbon) systems compared with the CBL-bound crystal structure’s luminal domain (orange ribbon). There is an observed difference in the luminal domain secondary structure (larger oval) of BtuB in the simulated membrane systems. Apo-sym reveals an α-helix between Gly82 and Gly92, whereas each OM system reveals a random coil along the same residues (see also Fig. S10). The random coil conformation brings Ser91, a CBL-interacting residue, closer to the conformation observed in the CBL-bound crystal structure. The smaller oval shows the Arg14 (gray sticks) lock mechanism (A) locked to the barrel wall, as found in the symmetric system, and (B) unlocked, bent toward the barrel interior. The unlocked conformation of Arg14 observed in the simulated OM systems is also found in the CBL-bound crystal structure (orange sticks). See the Supporting Material for movies of lumen extraction using SMD. To see this figure in color, go online.