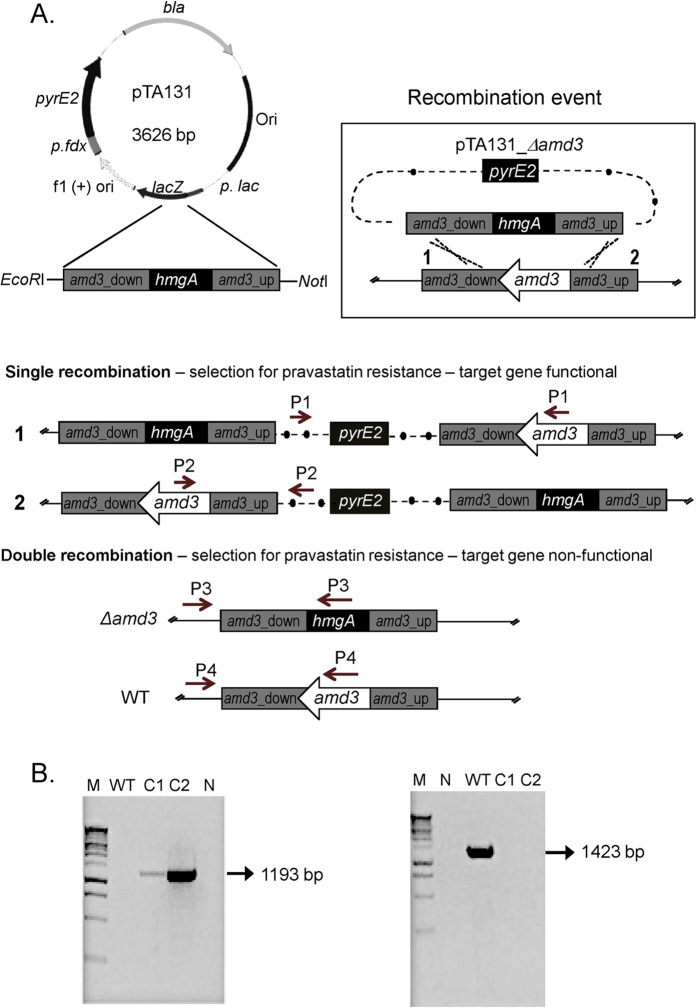
Figure 3. Construction of amd3 gene disruption.
(A) Pravastatin resistant cells arising from the transformation of pTA131_Δamd3 into wild-type Hrr. lacusprofundi can occur due to a single (plasmid insertion) or double (gene replacement) recombination event. Only the double recombination event produces a defective amd3 gene. Four groups of primers (P1, P2, P3 and P4) were used to determine if single or double recombination events occurred. The region denoted amd3_down corresponds to a 950 bp fragment containing the last 214 bp of amd3 and 736 bp of the downstream sequence, and the region denoted amd3_up corresponds to a 970 bp DNA fragment containing 225 bp of the 5′ coding region of amd3 and 745 bp of the upstream sequence (see Methods). In the section showing double recombination, the gene structure and diagnostic primers are shown for the amd3 disruption (Δamd3) and wild-type strain (WT). (B) A PCR product (1193 bp; left gel image) using the P3 primers was diagnostic of a double recombination event, whereas a PCR product (1423 bp; right gel image) using P4 primers was diagnostic of the wild-type genes being present. (A,B) Lane M, 1 kb DNA ladder; Lane N, no DNA (negative control); Lane WT, untransformed Hrr. lacusprofundi; Lane C1–C2, two strains with double recombination events. C2 was chosen as the Hrr. lacusprofundi Δamd3 strain. The results of other primer sets for C1 and C2 are show in Fig. S5.