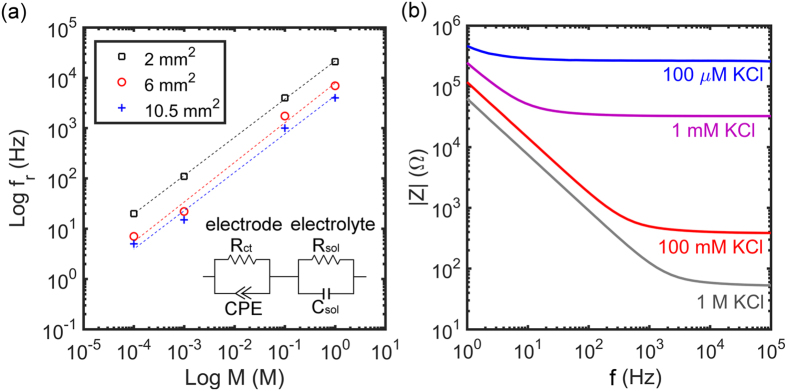
Figure 2. Impedance as a function of molarity.
(a) Maxwell-Wagner relaxation frequency as a function of molarity of an aqueous KCl solution. The frequency is extracted for the three different electrode areas. The dotted lines are a power law fit to the data with slope 0.9. Inset depicts the Randles equivalent circuit of an electrode-electrolyte interface, consisting of an interface capacitance, described by a constant phase element, CPE, shunted by a frequency independent charge transfer resistance, Rct, in series with the solution resistance, Rsol. The negligible solution capacitance, Csol, can be disregarded. (b) Impedance as a function of molarity of the aquous KCl electrolyte solution.