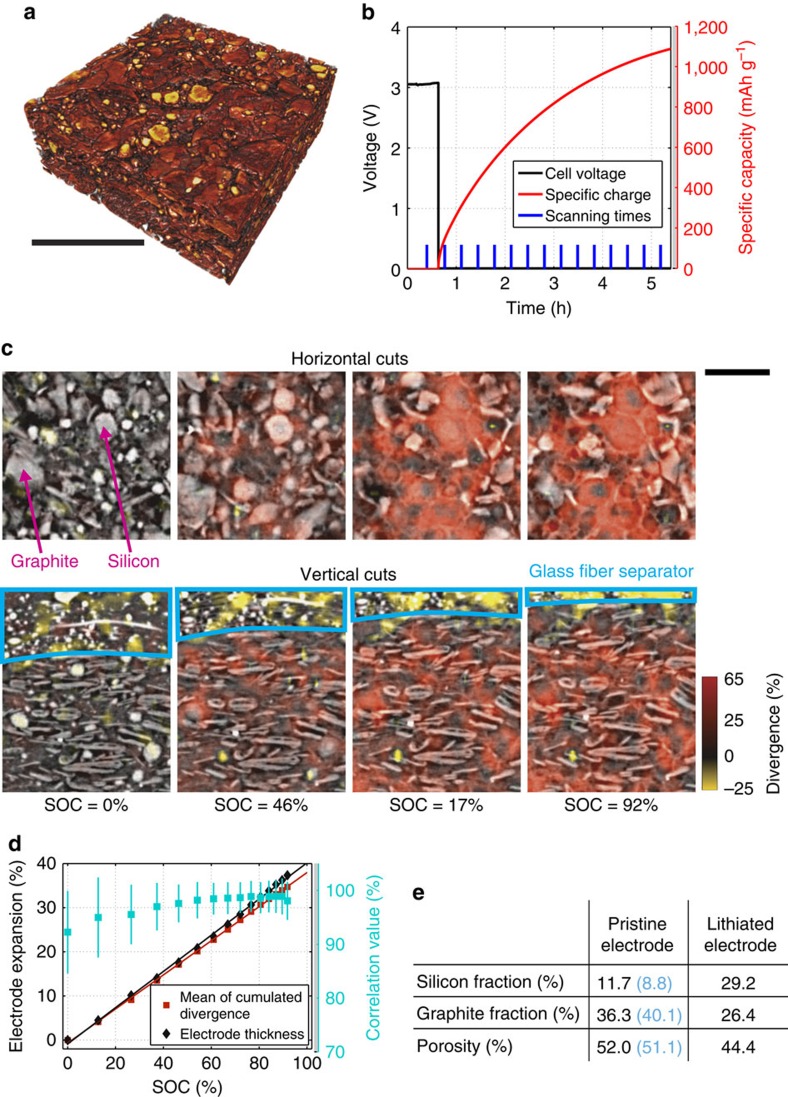
Figure 5. Silicon graphite composite electrode.
(a) Rendering from a part of the SiC electrode. Silicon particles are shown in yellow and graphite particles are shown in red. (b) Specific charge, voltage, and scanning times during operando electrochemical operation. The electrode is lithiated at a constant potential of 10 mV. Scale bar length: 100 μm. (c) Horizontal cuts (parallel to current collector) and vertical cuts (orthogonal to current collector) through the SiC electrode at different SOCs. The cumulated divergence is shown on top of each image, indicating local expansions (reddish) and contractions (yellowish) according to the scale bar. Scale bar length: 50 μm. (d) SiC electrode expansion based on (i) the mean cumulated divergence or alternatively (ii) the electrode thickness along the TP direction as a function of the SOC. The spatial averages of the correlation values at each SOC (blue squares) are an indicator for the goodness of the computed displacement fields. The vertical blue bars display the corresponding standard deviation of the correlation values. (e) Silicon, graphite and pore volume fractions in the pristine and the lithiated electrode. The values depicted in black are calculated based on the chemical composition of the electrode while the blue values are obtained from a segmentation of the tomographic data in the three phases.