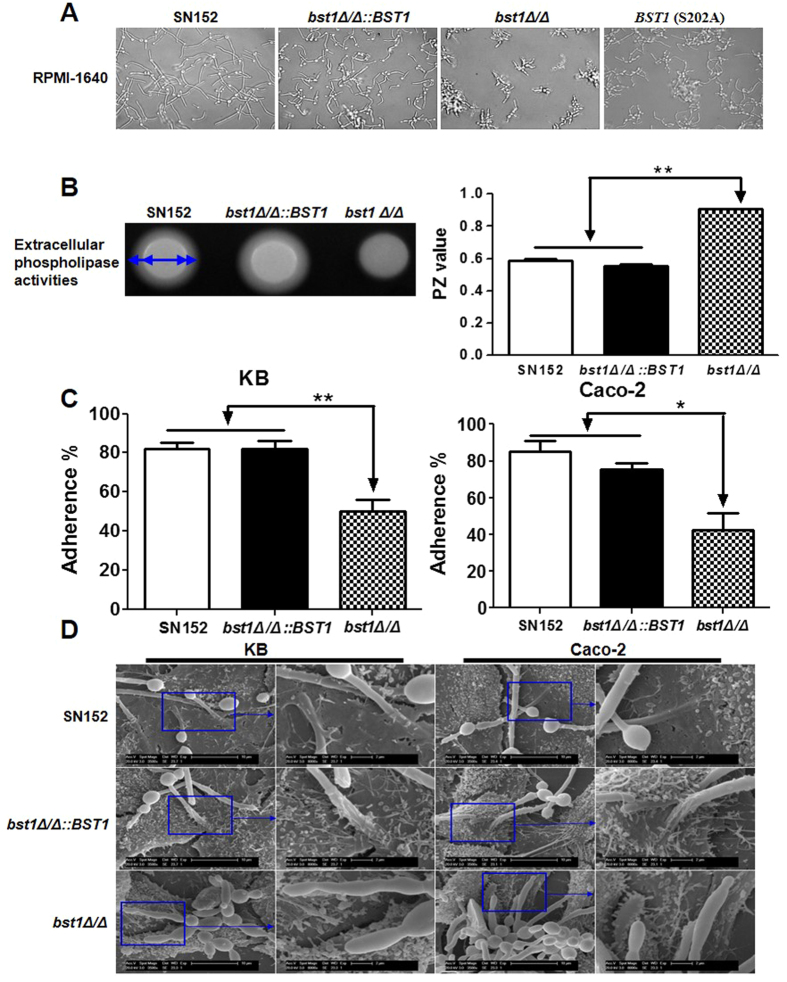
Figure 3. Deletion of BST1 gene impairs the invasive ability of C. albicans in vitro.
(A) Photomicrographs of parent (SN152), BST1-complemented (bst1Δ/Δ::BST1), bst1Δ/Δ null mutant (bst1Δ/Δ) and BST1 S202A mutant strains growing in liquid RPMI 1640 culture at 37 °C for 3 hours to induce the hyphal form. (B) The total extracellular phospholipase activities of parent (SN152), BST1-complemented (bst1Δ/Δ::BST1), bst1Δ/Δ null mutant (bst1Δ/Δ) strains were determined by growing them on egg yolk agar at 37 °C for 2 days and measuring the precipitation zone around each colony (left panel). The phospholipase activity zone (PZ) values of all the strains were calculated by the ratio of colony diameter to diameter of the dense white zone of precipitation around positive colonies (right panel), data represent mean (±SD) of triplicates from one representative experiment of three. **P < 0.01 (Error bars indicate SD. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test). (C) The rates of adherence of parent (SN152), BST1-complemented (bst1Δ/Δ::BST1), bst1Δ/Δ null mutant (bst1Δ/Δ) strains to human KB oral epithelial cells or intestinal Caco-2 epithelial cells were evaluated by co-incubating them for 60 minutes in six-well tissue culture plates, after which the adherent clones were counted. Data represent mean (±SD) of triplicates from one representative experiment of three. **P < 0.01 (Error bars indicate SD. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test). (D) Representative micrographs of scanning electron microscope (SEM) of KB and Caco-2 cells invaded or penetrated by parent strain (SN152), bst1Δ/Δ::BST1 and bst1Δ/Δ after 2 hours co-incubation.