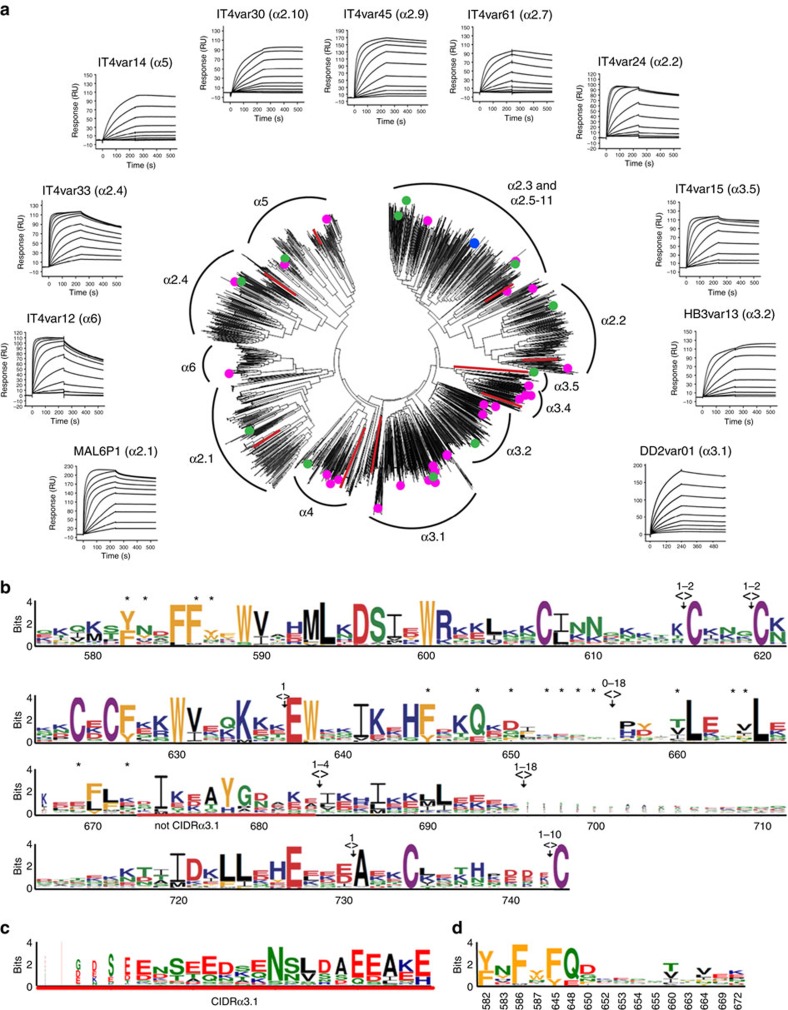
Figure 4. Extensive diversity in CD36 binding CIDRα domains.
(a) Sequence distance tree of 2386 full-length CIDRα2-6 domains. Red lines represent sequences from Plasmodium reichenowi. A blue circle marks the sequence of the crystallized CIDRα2.8 domain (also see Supplementary Fig. 8). Green circles mark sequences of recombinant CIDRα domains for which the affinity for CD36 binding were tested (corresponding SPR traces given). Pink circles mark sequences of CIDR domains previously demonstrated to bind CD36. Annotated clusters contained previously defined CIDRα2-6 subclasses. All tested domains from the CIDRα2-6 subclasses bind to CD36. (b) Sequences of the 2386 CIDRα domains were aligned and a sequence logo generated of residues equivalent to those found in the MCvar1 CIDRα domain (numbered as in MCvar1). Deletions (><) and insertions (<>) are indicated. The region underlined by a red line is found in all CIDRα2-6 domains except for CIDRα3.1. Residues labelled with * make direct contact to CD36. (c) The region found in CIDRα3.1 domains that replaces that underlined in red. (d) A sequence logo for the residues that make direct contacts to CD36.