Fig. 5.
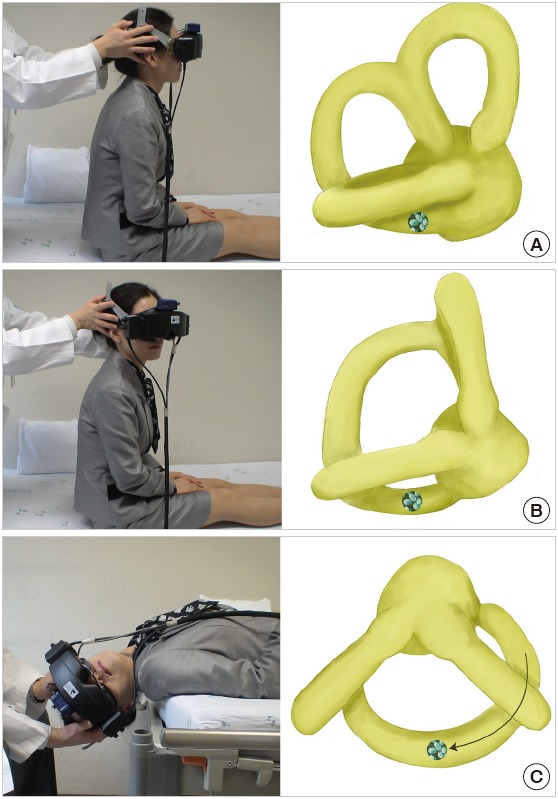
The Dix-Hallpike maneuver for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo usually arises from the posterior semicircular canal. After seating the patient upright (A), the head is turned 45° in the direction of the involved ear (B, right ear in this figure). The patient is then moved from the sitting to supine position, ending with the head hanging at 20° off the end of the examination table (C). The corresponding illustrations demonstrate the orientation of the semicircular canals and location of the otolithic debris in the posterior semicircular canal (viewed from the patient’s right side).
