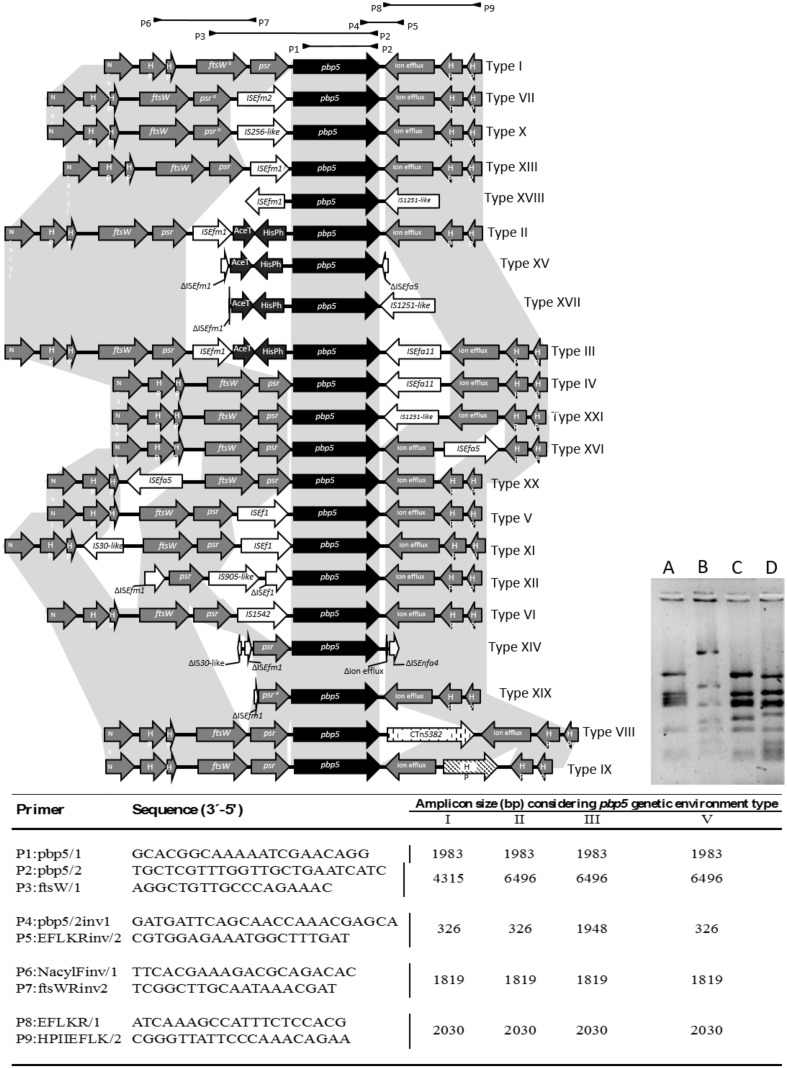
FIGURE 4.
Characterization of E. faecium pbp5 genetic environment by PCR and sequencing. The Roman numbers I, II, III, and V represent the different pbp5 genetic platforms detected in E. faecium from this study. The numbers IV, VI to XXI were detected in available genomes from GenBank database. The different types were named according to diversity of insertions sequences, genomic fragments or conjugative transposons within genes or intergenic regions. Mutations or recombinations within genes or intergenic regions were not considered for type classification. The Table indicates the primers used (designed for this study; P1/P2 described by Dahl et al., 2000) and the size of PCR amplicons from genetic environment of types I–III and V. The A, B, C and D lines of the bottom right side figure represent RFLP patterns of amplicon P3-P2 of mobile platforms I (pattern C) and II/III (pattern D) of isolates included in this study, when digested with DdeI restriction enzyme. The patterns A and B correspond to the amplicons of the recipient strains E. faecium BM4105RF and 64/3, respectively. a These gene has an extra stop codon within its sequence. Abbreviations: N-acyl, (N-acyl-glucosamine-6-phosphate-2-epimerase); HP (hypothetical protein); ftsW (cell cycle protein); psr, (pbp5 synthesis repressor); pbp5 (gene encoding penicillin binding protein 5); AceT (acetiltransferase); HisPh (Histidinol Phosphate Phosphatase).