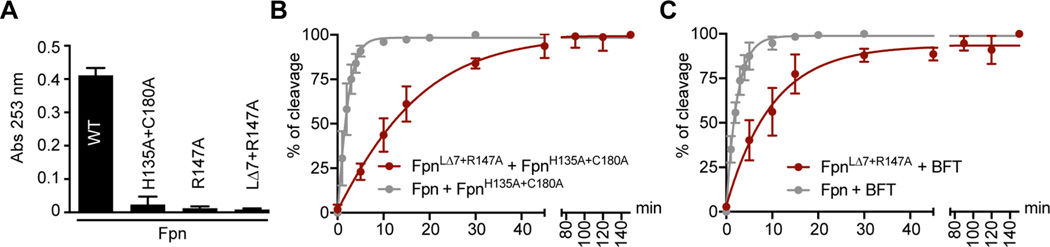
Figure 5.
Enzymatic activities of wild-type and mutant Fpn. (A) Absorbance at 253 nm representing the cleavage activities of 200 nM wild-type Fpn, FpnH135A+C180A, FpnR147A, or FpnLΔ7+R147A mutant proteins in the presence of 1250 µM synthetic substrate BAEE after incubation at 37 °C for 45 min. (B) Cleavage rate of purified FpnH135A+C180A used as a substrate in the presence of wild-type Fpn (gray) or FpnLΔ7+R147A (maroon). (C) Cleavage rate of purified BFT used as a substrate in the presence of wild-type Fpn (gray) or FpnLΔ7+R147A (maroon). In panels A and B, each cleavage experiment was performed three times; error bars represent standard deviations (SD) (mean ± SD).