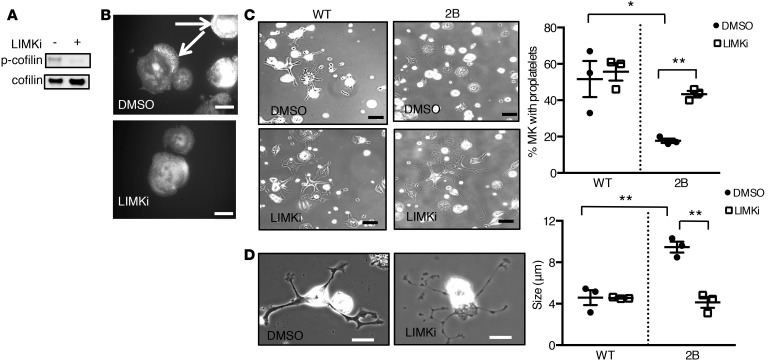
Figure 6. Inhibition of LIM kinase (LIMK) rescues proplatelet formation in type 2B mutant vWF/p.V1316M (2B) megakaryocytes (MKs).
(A) Western blot of phospho-cofilin (p-cofilin) in 2B MKs in the presence or absence of LIMK inhibitor (LIMKi). Mature MKs were incubated for 3 hours with 10 μM LIMKi or DMSO (1:500 vol/vol) and then lysed in SDS denaturing buffer. n = 3. (B) Representative images of 4 separate experiments of the actin structure (white arrows) in 2B MKs treated or not with LIMKi (10 μM). DMSO was used as control. Scale bars: 20 μm. (C) Mature MKs after thrombopoietin-induced differentiation in culture were incubated over a fibrinogen matrix for 5 hours in the presence or absence of LIMKi (10 μM). DMSO was used as control. Representative images of MKs forming proplatelets from 3 separate experiments. Scale bars: 50 μm. Quantification of the percentage of proplatelet-forming MKs in the presence or absence of LIMKi (right). The percentage of cells was measured in 3 separate experiments (50–80 MKs were analyzed/experiment). (D) Representative images (left) of 2B MKs in the presence or absence of LIMKi. Scale bars: 20 μm. Graph of the size of platelet-like structures (right) was measured in 3 separate experiments. Statistical significance was determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.