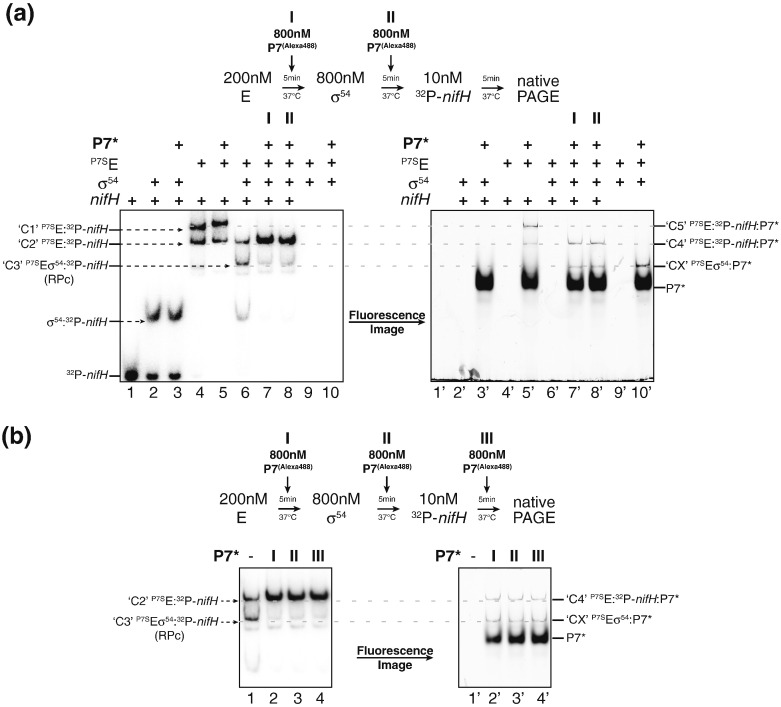
Fig. 4.
P7 inhibits RPc formation by the σ54-containing RNAP but does not fully dissociate the σ54–RNAP holoenzyme. Autoradiograph and fluorescent image of a 4.5% (wt/vol) native polyacrylamide gel showing results from EMSA experiment with 32P-labelled nifH promoter probe to demonstrate that P7 inhibits RPc formation by the σ54 holoenzyme conducted as previously described [16], [30]. (a) and (b) are essentially completed as in Fig. 3a, but the assays were conducted with Alexa488-labelled P7 (P7*) to determine the presence or absence of P7 in the different complexes detected in Fig. 3a. The Alexa488-labelled version of P7 was prepared as described in Ref. [31]. The components present in each lane are indicated above each image of the gel, and the schematic indicates the concentration of reaction components, time of addition, and incubation time. In (a and b), the migration positions of the different protein–protein and protein–DNA complexes are indicated (see text for details). Note that the gels analysed by radiography were dried prior to exposure to the phosphorimaging plate, whilst gels analysed by fluorescence were not dried.