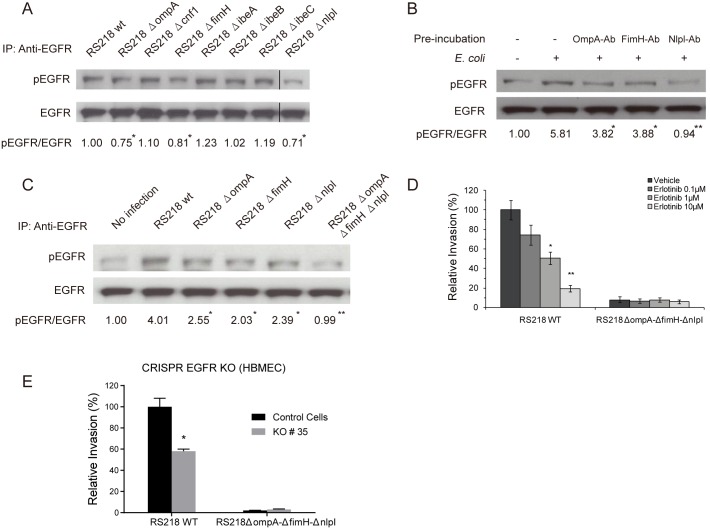
Fig 2. OmpA, FimH, and NlpI proteins are involved in meningitic E. coli-induced activation of EGFR.
(A) E. coli mutants with deletion of ompA, fimH or nlpI exhibited lower EGFR activation compared with wild-type RS218 in HBMEC monolayer. * p<0.05 compared to wild type bacteria. (B) Antibodies directed against OmpA, FimH, and NlpI decreased EGFR activation in response to E. coli in HBMEC. The bacteria were preincubated with the antibodies (with 1:10 dilution) individually for 1 h, and then added to HBMEC and incubated for 30 min for assessment of EGFR activation. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 compared to E. coli infection without antibody incubation. (C) EGFR activation in response to E. coli was not discernible with the triple deletion mutant (RS218ΔompAΔfimHΔnlpI), similar to that of the uninfected control HBMEC. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 compared with the E. coli RS218 wild-type infection. (D) Erlotinib inhibited the wild-type strain RS218 invasion of HBMEC in a dose-dependent manner, while it did not affect the HBMEC invasion by the triple mutant strain with deletion of ompA, fimH, and nlpI. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01. (E) E. coli wild-type strain RS218 invasion was significantly decreased in EGFR knock-out HBMEC (KO#35 cells) (* p<0.05), while the triple deletion mutant’s invasion did not differ between knock-out and control cells.