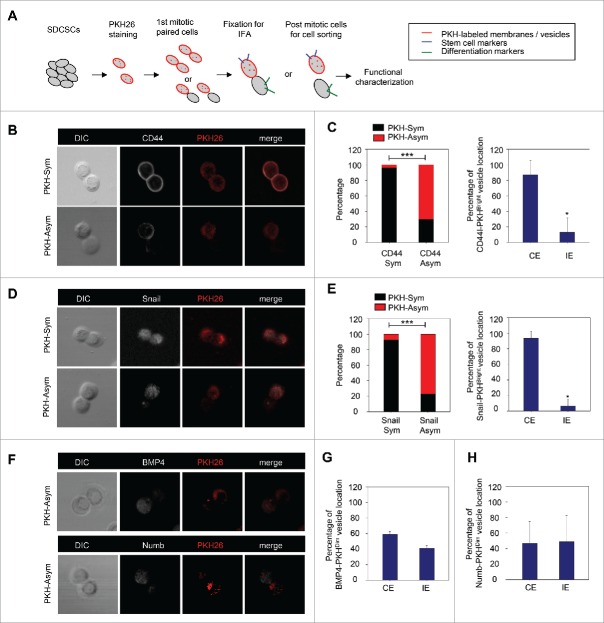
Figure 2.
The PKH26 vesicles co-segregate into daughter stem cells divided from SDCSCs. (A) A schema for illustrating the paired-cell assay. IFA, immunofluorescence analysis. (B) Representative images of paired-cell assay of serum-differentiated HT29 SDCSCs. CD44, white; PKH26 dye, red. PKH-Sym, symmetric segregation of PKH26-labeled vesicles; PKH-Asym, asymmetric segregation of PKH26-labeled vesicles. (C) Left: The percentage of PKH26 vesicles symmetry/asymmetry in serum-differentiated HT29 SDCSCs. CD44 Sym, symmetric CD44 segregation; CD44 Asym, asymmetric CD44 segregation. n (total counted cells over 2 independent experiments) = 66 and 37 for CD44 Sym and CD44 Asym, respectively. ***, p < 0.001 (χ2 test). Right: The percentage of CD44 and PKH26 vesicles co-expression (CE) or inverse expression (IE) in PKHBright daughter cells undergoing asymmetric cell division. Data represent mean ± SD n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 (Student's t test). (D) Representative images of paired-cell assay of serum-differentiated HT29 SDCSCs. Snail, white; PKH26 dye, red. (E) Left: The percentage of PKH26 vesicles symmetry/asymmetry in serum-differentiated HT29 SDCSCs. Snail Sym, symmetric Snail segregation; Snail Asym, asymmetric Snail segregation. n (total counted cells over 2 independent experiments) = 87 and 38 for Snail Sym and Snail Asym, respectively. ***, p < 0.001 (χ2 test). Right: The percentage of Snail and PKH26 vesicles co-expression (CE) or inverse expression (IE) in PKHBright daughter cells undergoing asymmetric cell division. *, p < 0.05 (Student's t test). (F) Representative images of paired-cell assay of serum-differentiated HT29 SDCSCs. BMP4 and Numb, white; PKH26 dye, red. (G) The percentage of BMP4 and PKH26 vesicles co-expression (CE) or inverse expression (IE) in PKHDim daughter cells undergoing asymmetric cell division. (H) The percentage of Numb and PKH26 vesicles co-expression (CE) or inverse expression (IE) in PKHDim daughter cells undergoing asymmetric cell division.