Fig 2. The PC model shows unrealistically high jitter when tracking stimuli.
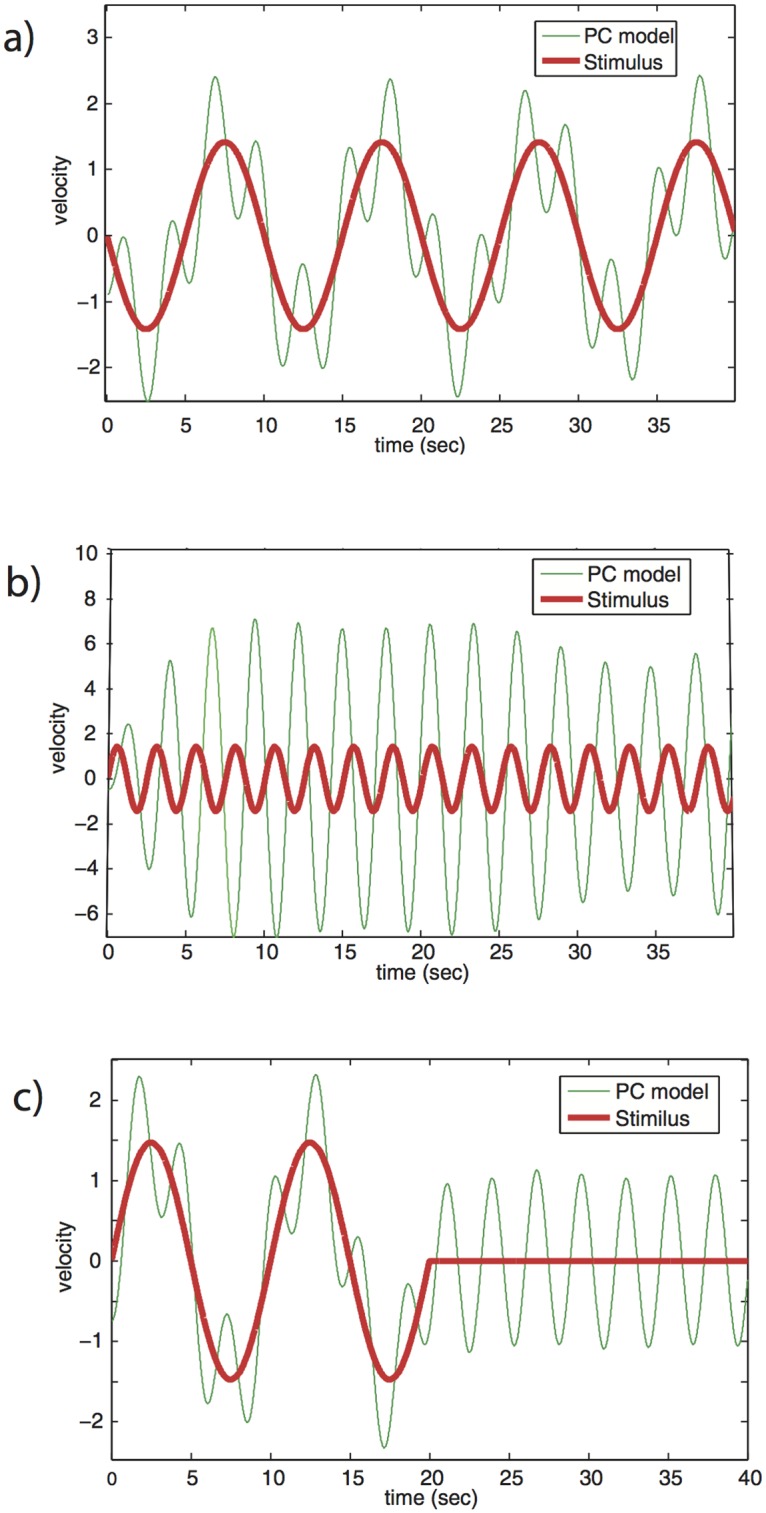
(a) Tracking a stimulus with f(0) = 0.1, A21(0) = −1, initial velocity v1(0) = −1, v2(0) = −0.5. Jitter amplitude is about 5-fold higher than observed in Fig 1a. (b) at high stimulus frequency (not obeying ), f(0) = 2, A21(0) = 1.5, v1(0) = 0.5, v2(0) = −0.5, jitter increases to an amplitude to be almost 4 times higher than the stimulus and 20-fold higher than observed in Fig 1a. Such phenomena occur for a wide range of parameters. Here we used k = 8, g = 0.3 and initial amplitudes A1n(0) = 0. (c) When stimulus suddenly stops, PC model does not settle to zero velocity. Here we use three periods in the predictor, and f(0) = 0.1, A21(0) = −1, v1(0) = 0.5, v2(0) = −0.5 and all other initial amplitudes Ain(0) = 0.
