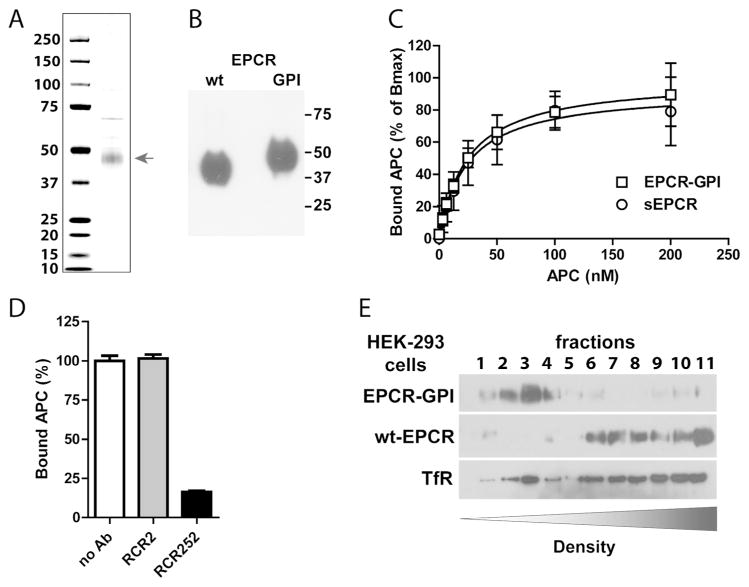
Figure 3. Purification and APC binding to EPCR-GPI.
EPCR-GPI expressed in HEK-293 cells was purified from cell lysates. (A) Coomassie stain and (B) Western blot of purified EPCR-GPI under non-reducing conditions. (C) APC binding to recombinant soluble EPCR (sEPCR; circle) and EPCR-GPI (square). Signals were corrected for aspecific binding of APC to wells without EPCR. Data was fitted to a non-linear regression curve for one-site specific binding to calculate the Bmax and apparent KD, followed by normalized of the data to the corresponding Bmax. (D) Specificity of APC binding to EPCR-GPI using the blocking (rcr-252) and non-blocking (rcr-2) control anti-EPCR antibodies (both used at 20 μg/ml). (C-D) Shown are mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. (E) Representative experiment of cell membrane fractionation on a density gradient of EPCR-GPI or wt-EPCR transfected HEK-293 cells. TfR denotes the transferrin receptor.