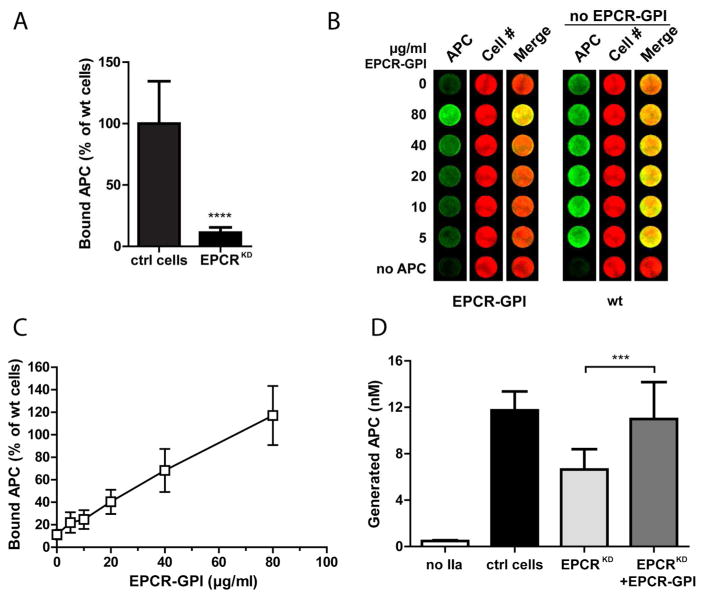
Figure 6. Improvement of APC binding and protein C activation by EPCR-GPI painting.
EPCR-GPI’s ability to support APC binding and PC activation on EPCRKD cells was determined. (A) APC binding to the surface of EA.hy926 EPCRKD cells was detected by on-cell Western and normalized to wild type EA.hy926 cells (ctrl cells). (B) Binding of APC to EPCRKD cells painted with 0–80 μg/ml EPCR-GPI for 90 minutes. Painted EPCRKD cells (paint) and untreated wild type EA.hy926 cells (wt) were stained for APC (green) and cell number (red). Shown is a representative image of three independent experiments. Note that wild type EA.hy926 cells did not receive paint. (C) Quantification of APC binding to painted EPCRKD cells. APC levels were corrected for background signal (no APC) and normalized for cell number. APC binding to untreated wild type EA.hy926 cells was set at 100%. (D) PC activation on EPCRKD cells painted with 80 μg/ml EPCR-GPI (EPCRKD+EPCR-GPI), untreated EPCRKD (EPCRKD), and wild type EA.hy926 cells (ctrl cells). PC activated by thrombin in the absence of cells was subtracted as background. For all experiments mean ± SD of three independent experiments are shown. *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001.