Figure 1. Depletion of FGFR2 or CD44 suppressed tumor sphere formation and tumor growth.
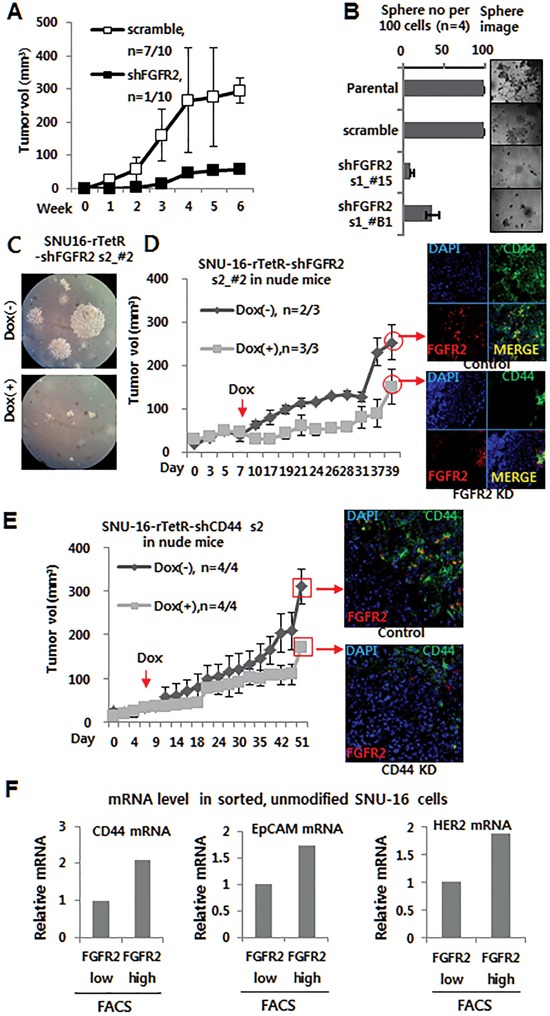
A. A shRNA s1-mediated FGFR2 KD suppressed tumor growth in nude mice (n = 10). While scrambled cells formed tumors (329 mm3) in seven of 10 mice, stable FGFR2 KD cells supported tumor growth in only one of 10 mice (See Figure S2 for detailed images of all 10 mice). B. FGFR2 KD suppressed tumor sphere formation in shRNA s1 clones (#15 and B1). C. Doxycycline (Dox)-induced FGFR2 KD in vitro suppressed colony formation in soft agar. D–E. Dox-induced KD of FGFR2 (D) or CD44 (E) in vivo suppressed tumor growth in nude mice. Dox (2 mg/ml in water) was administrated daily to mice with sizable tumors (50–100 mm3; n = 3). FGFR2 KD or CD44 KD in the formed tumor masses was validated by immunofluorescence (IF) staining (shown on the right). F. Higher levels of CD44, EpCAM, and Her2 mRNAs were found in flow cytometry-sorted FGFR2+/hi fractions than FGFR2−/lo fractions.
