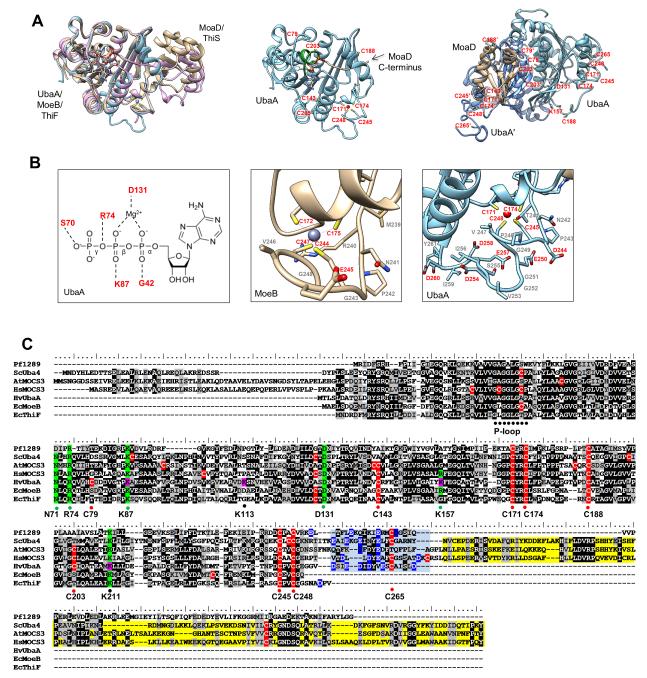
Figure 3. UbaA 3D-structural model and multiple amino acid sequence alignment.
(A) Ribbon diagram UbaA (blue) predicted structure and its superimposition onto the crystal structures of E. coli covalent acyl-adenylate form of the MoeB:MoaD complex (gold) (1JWB) and monomeric half of the ThiF:ThiS complex (purple) (1ZUD). Coordinating AMP, Zn2+ ligands and UbaA P-loop (green) are highlighted. UbaA homodimer is designated by light (UbaA) and dark (UbaA’) blue ribbon diagram with cysteine and other residues highlighted. (B) From left to right: i) schematic representation showing conserved residues of the UbaA adenylation domain predicted to coordinate Mg-ATP; ii) ribbon diagram of MoeB C-terminal region including the Cys tetrad residues (C172-X2-C175-Xn-C244-X2-C247) that coordinate Zn2+; and iii) ribbon diagram of 3D-model of UbaA C-terminal region that includes Cys tetrad residues (C171-X2-C174-Xn-C245-X2-C248) and acidic residues (D244, E250, D254, E257, D258, and D260) which could coordinate Zn2+. (C) Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of UbaA with homologs of the E1/MoeB/ThiF superfamily. Predicted catalytic cysteine (C188), conserved Cys-tetrad (C171, C174, C245, C248), and less conserved cysteine residues (C79, C143, C203, and C265) of UbaA are indicated in red. UbaA residues of the adenylation domain found important for ATP binding (K87 and D131) and other activities (R74 and N71) are highlighted in green. UbaA lysine residues modified by Ubl bonds are indicated in pink, with K87 and K157 further highlighted in green to indicate their important role in catalytic activity. Highlighted in blue is the acidic C-terminal tail common to archaeal UbaA homologs and linker to the rhodanese domain of eukaryotic Uba4/MOCS3 homologs (the latter highlighted in yellow). Abbreviations with UniProt accession numbers: Hfx. volcanii HvUbaA (sp∣D4GSF3∣), E. coli EcMoeB (sp∣P12282∣), E. coli EcThiF (sp∣P30138∣), P. furiosus Pf1289 (tr∣Q8U1C8∣), yeast ScUba4 (sp∣P38820∣), human HsMOCS3 (sp∣O95396∣), Arabidopsis thaliana AtMOCS3 (sp∣Q9ZNW0∣).