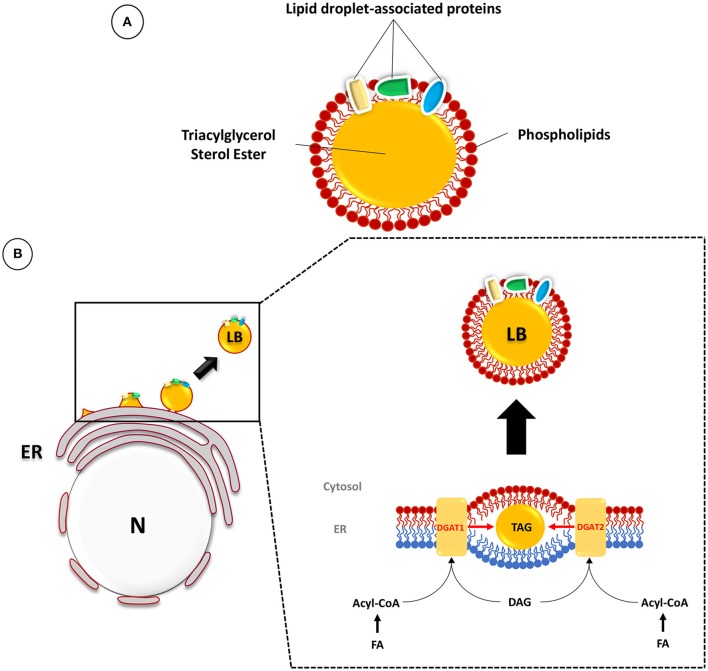
Figure 1.
Composition and biogenesis of lipid bodies (LB) in mammalian cells. (A) The LB is composed of a core of TAG and sterol esters surrounded by a phospholipid monolayer and associated proteins. (B) TAG synthesis occurs between the two membrane leaflets of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) (inner leaflet in blue and outer leaflet in red). The prevailing model suggests that host LB originate at the ER, where fatty acids (FA) are resynthesized to form triacylglycerol (TAG) and sterol esters. These compounds accumulate in the hydrophobic space between the two leaflets (in red: outer leaflet; in blue: inner leaflet) of the ER bilayer membrane. The final step is catalyzed by the diacylglycerol acyltransferases DGAT1 and DGAT2. The conversion of diacylglycerol (DAG) and Acyl-CoA into TAG leads to the formation of a lipid globule which will expand dynamically and finally be released into the cytosol as a mature LB surrounded by phospholipids of the cytosolic leaflet of the ER bilayer membrane. Adapted from (Murphy, 2001; Kassan et al., 2013; Pol et al., 2014).