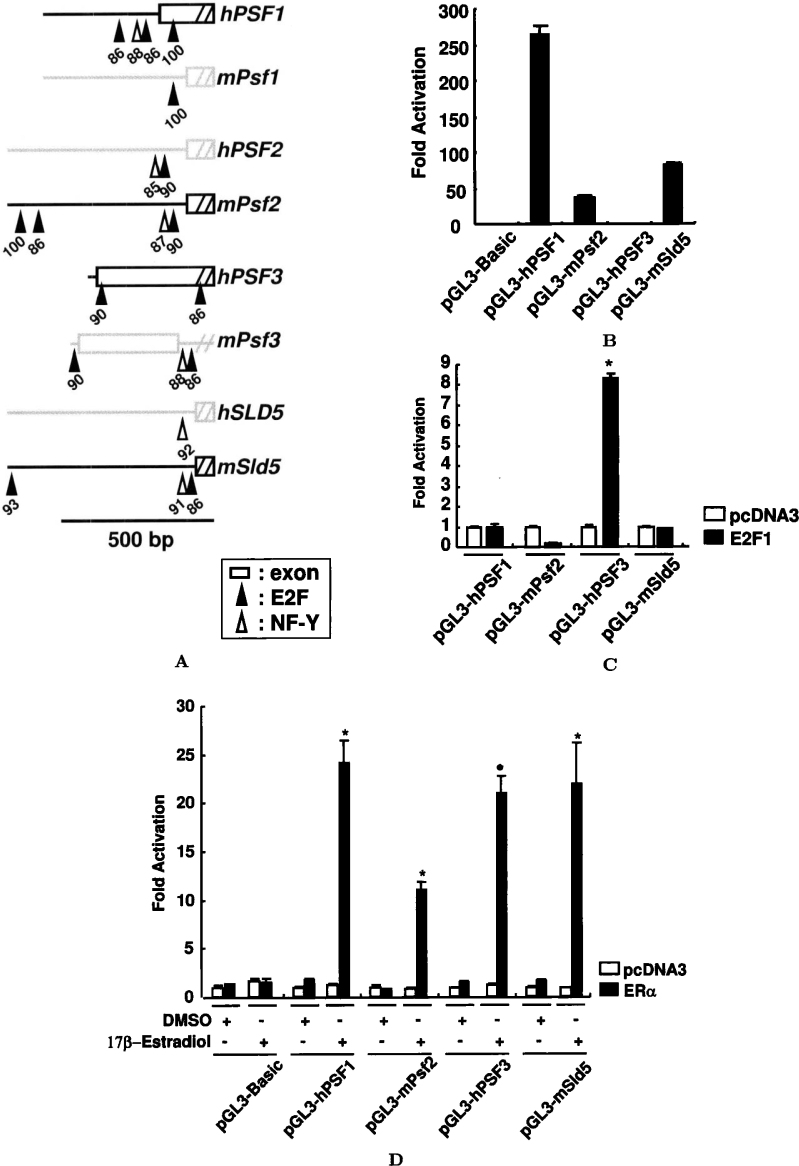
Fig. 2.
Transcriptional regulation of the human and mouse GINS genes. A. Schematic representation of the vicinity of the transcription start sites of the human and mouse GINS genes. The putative transcription factor E2F- (closed isosceles triangles) and NF-Y-binding sites (open isosceles triangles) are indicated with their scores (maximum score 100) calculated by the Transfac program. Exon 1 (open boxes) is indicated. Scale bar equals 500 bp. B. Human and mouse GINS promoter activities in asynchronously growing human cells. HeLa cells were transfected with 200 ng of reporter constructs and 400 ng of the expression vector for E2F1, together with 0.6 ng of pRL-TK. The pcDNA3 vector was used as the negative control. At 48 h after the transfection, the cells were harvested, and extracts were prepared to measure the firefly and Renilla luciferase activities. Values are represented as relative luciferase activities, with that of pGL3-Basic being taken as 1. C. The E2F-binding motif of the PSF3 promoter is sufficient to confer responses to ectopic E2F expression. The experiment was performed as described in panel B. Values are represented as relative luciferase activities, with that of the control vector pcDNA3 being taken as 1. Statistically significant (P < 0.05) induction is indicated by an asterisk. D. E2-induced activation of GINS promoter constructs in HeLa cells. Cells were transfected with the indicated reporter plasmids and pcDNA3 or pSG5-ERα expression vector, and the effects of E2 or DMSO on the luciferase activities were determined. Results are expressed as mean±S.D. for at least three triplicate determinations for each treatment group. Statistically significant (P < 0.05) induction is indicated by an asterisk.