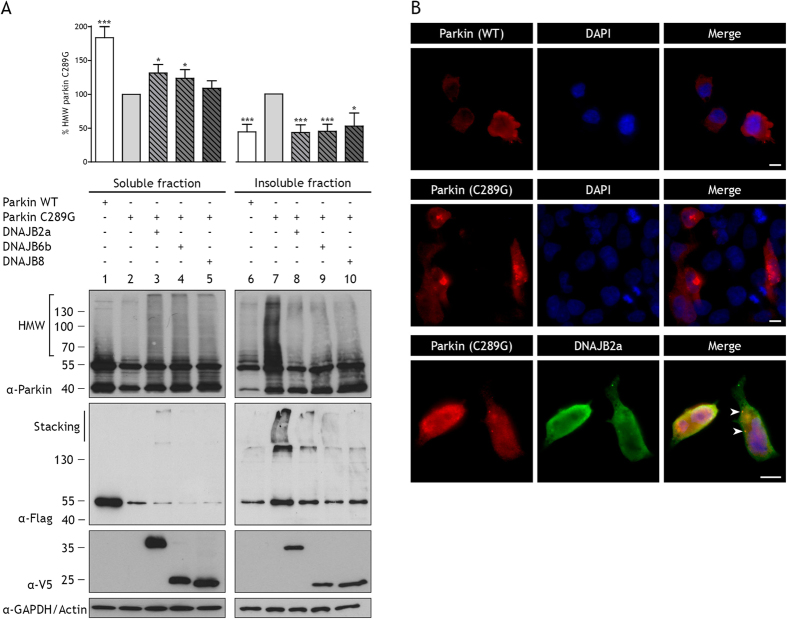
Figure 1. DNAJB2a, DNAJB6b, or DNAJB8 can prevent aggregation of parkin C289G.
(A) HEK293 cells were transfected with flag-tagged parkin WT, flag-tagged parkin C289G, or co-transfected with flag-tagged parkin C289G and V5-tagged DNAJB2a, DNAJB6b, or DNAJB8. Expression of chaperones was induced with tetracycline. Triton X-100 (TX-100) soluble and insoluble fraction were obtained 24 hours after transfection. Parkin WT and C289G were assessed with anti-parkin and anti-flag antibodies on Western blot and analysed for parkin C289G high molecular weight species and normalised to parkin C289G (*p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; n > 4 independent samples, mean ± SEM). In the TX-100 insoluble fraction, high molecular weight (HMW) species of parkin C289G are observed. Co-transfection with DNAJB2a, DNAJB6b, or DNAJB8 prevents formation of parkin C289G HMW species. Anti-parkin antibodies detect full-length parkin and an N-terminally truncated isoform (also removing the flag-tag), generated due to an internal start site, showing an extra band around 42 kDa68. The anti-flag antibodies recognize predominantly the full-length parkin protein. Expression of chaperones was detected with anti-V5 antibodies. GAPDH was used as a loading control for the soluble fraction. (B) Representative immunofluorescence pictures of cells co-transfected with flag-tagged parkin WT or parkin C289G (red) and V5-tagged chaperones (green). DAPI staining is shown in blue. Bar represents 10 μm. Parkin WT shows a diffuse pattern throughout the cytoplasm. Parkin C289G forms aggregates mainly concentrated into large perinuclear inclusions. Co-transfection with DNAJB2a reveals clearance of parkin C289G aggregates and co-localization of DNAJB2a with parkin C289G, indicated by arrowheads.