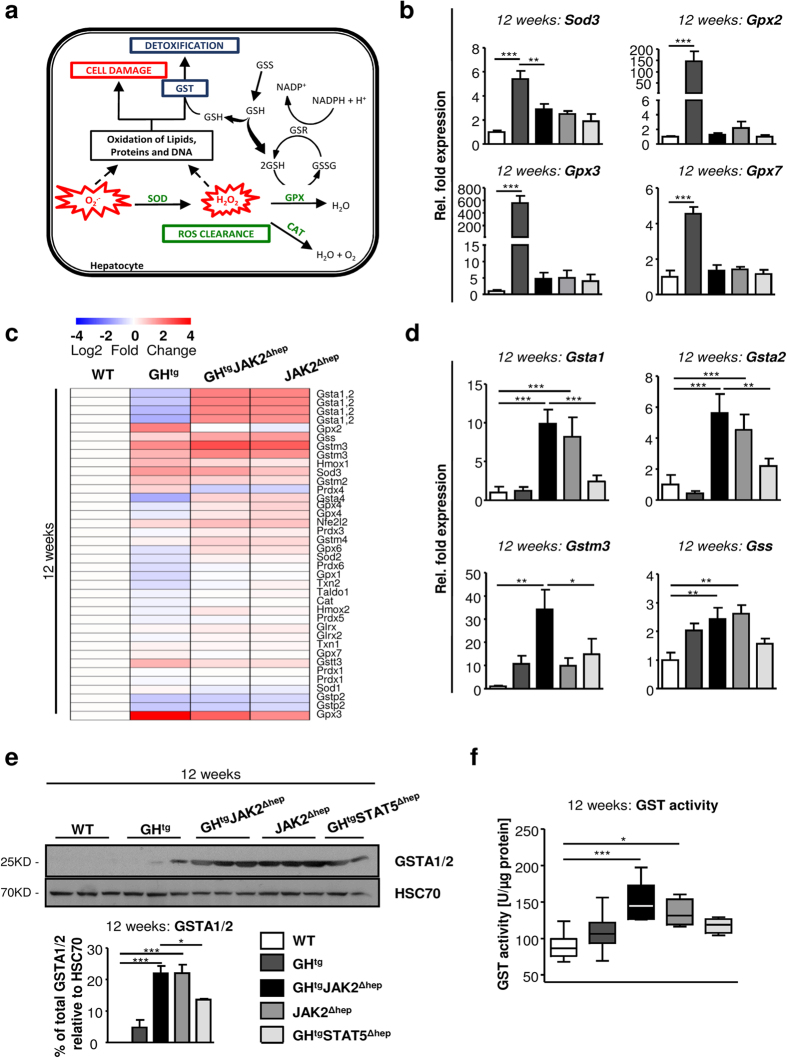
Figure 5. Genetic deletion of hepatic Jak2 results in increased expression and activity of detoxifying enzymes.
(a) Schematic overview of the antioxidative defence system. SOD, CAT and GPX are the primary antioxidant enzymes which inactivate ROS into intermediates. GST catalyses the conjugation of the reduced form of GSH to oxidised products to detoxify oxidised lipids, proteins and DNA (H+: hydrogen ion, SOD: superoxide dismutase, CAT: catalase, GPX: glutathione peroxidase, GSSG: oxidized glutathione, GSH: glutathione, GSS: glutathione synthetase, GSR: glutathione reductase, GST: glutathione S-transferase). (b) By means of qRT-PCR, mRNA levels of Sod3, Gpx2, Gpx3 and Gpx7 involved in antioxidant response were measured in livers at 12 weeks of age (n = 6/genotype). Ct values were normalised to Gapdh and Rpl12a. (c) At 12 weeks of age transcriptome analysis of genes coding for enzymes involved in antioxidant defence. (d) mRNA expression levels of Gsta1, Gsta2, Gstm3 and Gss at 12 weeks of age (n = 6/genotype). Ct values were normalised to Gapdh. (e) Representative Western blot analysis of whole liver homogenates and Western blot quantification of GSTA1/2 from 12-week-old animals. As a loading control HSC70 is shown (n ≥ 2/genotype). Scans of blots are presented in Supplementary Fig. S10. (f) GST activity was assessed in livers from 12-week-old mice using a colorimetric assay (n ≥ 6/genotype). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.001.